Cardiology/Vascular
A Case Report of May-Thurner Syndrome Identified on Abdominal Ultrasound
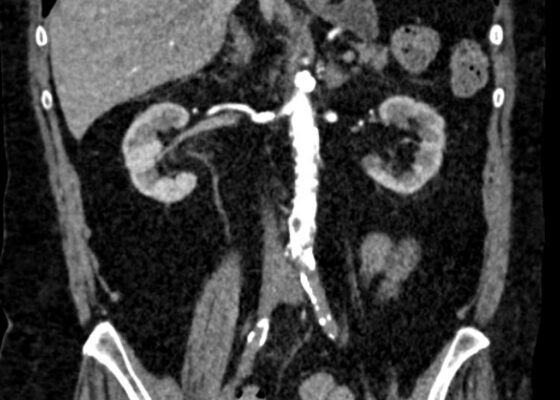
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8C64KThe patient initially received a venous doppler ultrasound that showed no evidence of a right or left femoropopliteal venous thrombus. Due to the high suspicion of a DVT given the symmetric swelling to the entire limb and acute onset of pain, a CTV was ordered. The transverse view of the CTV showed chronic thrombotic occlusion of the proximal left common iliac vein associated with compression from the right common iliac artery (figure 1, transverse image of CTA), as well as thrombotic occlusion of the left internal iliac vein tributary and corresponding left ascending lumbar vein. Given the previously mentioned clinical context, these features suggested the diagnosis of May-Thurner syndrome.
Unravelling the Mystery of a Continuous Coil: A Case Report
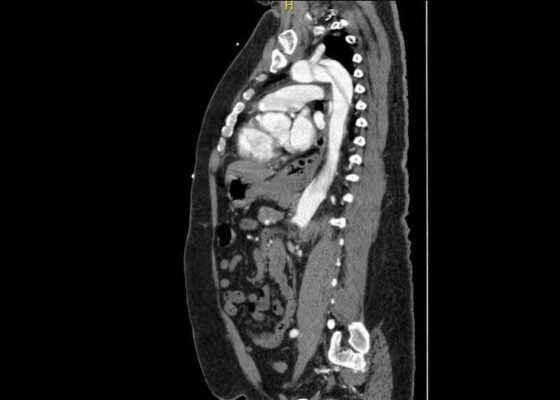
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8PM00A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis with intravenous contrast for evaluation of new onset abdominal pain and distension was obtained in the emergency department. The axial view (CT Image A) shows the coil pack from the prior coil-assisted retrograde transvenous obliteration procedure, seen in the left renal vein and gastric varix (red arrow). The path of the coil (yellow arrow) is continuous into the inferior vena cava (CT Image B). It is then seen (CT Image C) situated in the right ventricle (green arrow). Finally, the coil pack is seen in a coronal section, demonstrating its upward path (blue arrow) in the inferior vena cava. (CT Image D). Additional findings included ascites with advanced cirrhosis. As noted in the CT images, a vascular embolization coil was seen within a varix near the junction of the left renal vein. This appeared to have unraveled and extended superiorly into the inferior vena cava and ultimately into the right atrium and right ventricle.
Principles of Hypotensive Shock: A Video Introduction to Pathophysiology and Treatment Strategies
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8MS84By the end of this module, participants should be able to: 1) review basic principles of cardiovascular physiology; 2) describe the 4 general pathophysiologic mechanisms of hypotensive shock; 3) recognize various etiologies for each mechanism of hypotensive shock; 4) recognize differences in the clinical presentation of each mechanism of hypotensive shock; 5) cite the basic approach to treatment for each mechanism of hypotensive shock.
A Lecture to Teach an Approach and Improve Resident Comfort in Leading Resuscitation of Young Infants in the Emergency Department
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8H36JBy the end of this lecture, participants should be able to: 1) apply a consistent approach to the initial resuscitation of a critically ill young infant in the emergency department; 2) select appropriate medications and equipment for use in resuscitation of critically ill young infants; 3) describe the components of the Pediatric Assessment Triangle,6 which can be used to identify critically ill infants and children; 4) improve comfort in resuscitating young infants in the emergency department.
Initial Management and Recognition of Aortoiliac Occlusive Disease, A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87M0ZComputerized tomography with angiography (CTA) of the entire aorta demonstrated an occluded distal infrarenal aorta with extension into the bilateral common femoral arteries (red outline), lack of flow through femoral arteries (yellow outline) and trickle flow reconstituted distally consistent with aortoiliac occlusive disease (blue outline). Some small segments of the proximal celiac axis showed signs of occlusion (purple outline). A short segment of non-specific bowel wall thickening, which may have been related to ischemic changes, was also seen (not seen on images). The included coronal slice shows the extent of the bilateral occlusive burden, with three-dimensional reconstruction emphasizing the same findings.
A Case Report of Aortic Dissection Involving the Aortic Root, Left Common Carotid Artery, and Iliac Arteries
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8V93KComputed tomography angiography (CTA) of the thoracic and abdominal aorta revealed an aortic dissection of the ascending aorta, with a dissection flap starting from the aortic root/aortic annulus (yellow arrows), extending into the aortic arch (light blue arrowhead) and involving the left common carotid artery (purple arrow), left subclavian artery (pink arrow), extending to the descending aorta (red arrows), and into the bilateral iliacs (green arrows). The true lumen (red star) and false lumen (blue star) created by the dissection flap can best be seen in the axial views.
Cardiac Arrest in an Adolescent with Pulmonary Embolism
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8135TABSTRACT: Audience: The target audience of this simulation is emergency medicine residents and medical students. The simulation is based on a real case of a 13-year-old female who presented with seizures and hypoxia and was ultimately diagnosed with pulmonary embolism. The case highlights diagnosis and management of an adolescent with new onset seizures, deterioration in status, and treatment options in