Cardiology/Vascular
My Broken Heart
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J85W7RBy the end of this simulation session, learners will be able to: 1) assess the hemodynamics of an LVAD patient by using a Doppler to determine mean arterial pressure, 2) Manage an arrhythmia in an LVAD patient with a suction event by addressing preload, 3) Identify and treat the source of hypovolemia (a massive lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage), 4) Perform clear closed-loop communication with other team members.
Stabilization of Cardiogenic Shock for Critical Care Transport, a Simulation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82354ABSTRACT: Audience: This simulation is designed for critical care transport providers but can be easily adapted for the inpatient setting. It is applicable to an interdisciplinary team including nurses, respiratory therapists, medical students, emergency medicine residents, and emergency medicine attendings. Introduction: Cardiogenic shock carries an incredibly high burden of morbidity and mortality. Acute myocardial infarction accounts for 81% of cardiogenic
Journal Court: A Novel Approach to Incorporate Medicolegal Education into an Emergency Medicine Journal Club
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8093TBy the end of this exercise, participants should: 1) identify the four necessary elements for a malpractice claim, 2) understand the basic structure of medical malpractice litigation, and 3) critically analyze medical literature representing diverging viewpoints or conclusions.
Drowning Complicated by Hypothermia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QS7PAt the conclusion of the simulation session, learners will be able to: 1) obtain a relevant focused history, including circumstances of drowning and/or cold exposure; 2) outline different clinical presentations of hypothermia, loosely correlated with core temperature readings; 3) discuss management of hypothermia, including passive external rewarming, active external rewarming, active internal rewarming, and extracorporeal blood rewarming; 4) discuss pathophysiology of drowning; 5) identify appropriate disposition of patients who present after drowning; and 6) identify appropriate disposition of hypothermic patients.
A Case Report of Right Atrial Thrombosis Complicated by Multiple Pulmonary Emboli: POCUS For the Win!
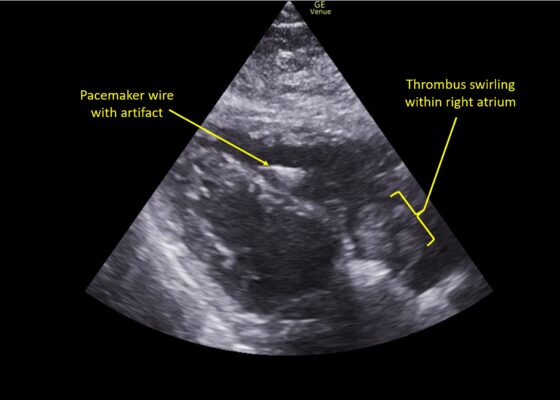
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TM07Pulmonary POCUS was performed by the ED physician (GE Venue, C1-5-RS 5MHz curvilinear transducer), and lung examination was unremarkable with no pleural effusion, pneumothorax, or infiltrate. Subxiphoid views (GE Venue, 3Sc-RS 4MHz phased-array transducer) were obtained because this patient’s COPD with severe pulmonary hyperexpansion made parasternal and apical 4-chamber views suboptimal. A large thrombus can be seen within the right atrium (movie 1, images 1, 2). This has a serpiginous, rounded appearance and is mobile, appearing to swirl within the right atrium with intermittent extrusion through the tricuspid valve. A pacemaker wire is also visible within the right ventricle as a non-moving, hyperechoic, linear structure with posterior enhancement artifact. Pericardial effusion is not present.
Going in Blind: A Common Scenario in an Uncommon Situation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8RS8CBy the end of this simulation, learners will be able to (1) evaluate and treat a patient experiencing myocardial infarction and subsequent cardiac arrest during a power outage, (2) describe the local protocols for managing patient care during a power outage, (3) demonstrate the ability to coordinate a medical team during a simulated power outage in an emergency department with limited resources, (4) manage a cardiac arrest patient by following Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) protocols for bradycardia and ventricular fibrillation, and (5) justify the urgency of transfer to a certified ST segment elevation myocardial infarction center/cardiac intensive care unit, referencing the recommended 120-minute door-to-balloon time.
A Realistic, Low-Cost Simulated Automated Chest Compression Device
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8M63CBy the end of this educational session using a resuscitation trainer or high-fidelity manikin, learners should be able to: 1) recognize appropriate application of simulated ACCD to an ongoing resuscitation case; 2) demonstrate proper positioning of simulated ACCD in manikin model and 3) integrate simulated ACCD to provide compressions appropriately throughout cardiac arrest scenario.