Videos
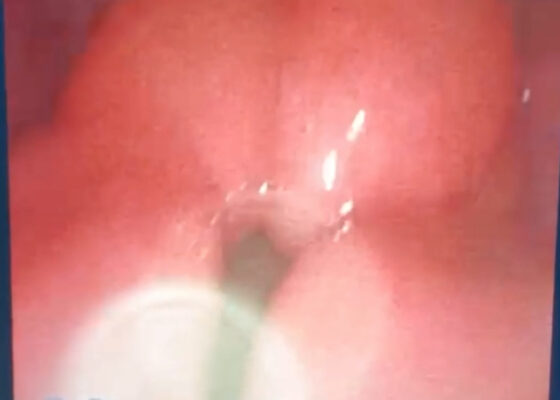
A Case Report of Epiglottitis in an Adult Patient
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QM09At the time of presentation to the ED, laboratory results were significant for leukocytosis to 11.8 x 109 white blood cells/L and a partial pressure of carbon dioxide of 52 mmHg on venous blood gas. Computed tomography (CT) of the soft tissue of the neck with contrast showed edematous swelling of the epiglottis and aryepiglottic fold with internal foci of gas (blue arrow) and partial effacement of the laryngopharyngeal airway and scattered cervical lymph nodes bilaterally (Figure 1). Findings were consistent with epiglottitis containing nonspecific air. Additionally, the pathognomonic “thumbprint sign” (yellow arrow) was found on lateral x-ray of the neck (Figure 2). The CT findings as shown in figure 3 illustrate lateral view of the swelling of the epiglottis, gas, and blockage of the airway.
A Woman with Arm Spasms
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VP88The patient had a witnessed episode of isolated left upper extremity jerking, shown in the video, during which she was completely awake and conversant. Lab results were significant for serum glucose of 1167 mg/dL, no anion gap, and negative serum/urine ketones. She had a computed tomography (CT) of the head that did not show any acute pathology, and underwent a brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) without any signs of stroke or other pathology, shown below.
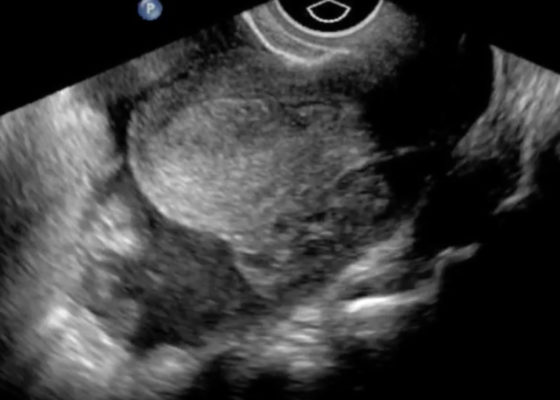
Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8SG6TThe patient’s serum beta-hCG was 5,637 mIU/mL. The transvaginal ultrasound showed an empty uterus with free fluid posteriorly in the pelvis and Pouch of Douglas (00:00). A 4.5 cm heterogeneous mass was visible in the left adnexa concerning for an ectopic pregnancy (00:10).
Atrial Myxoma
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87P45Bedside ultrasound revealed the presence of a left atrial mass that appeared to be tethered to the mitral valve. The mass was best viewed on ultrasound in the apical four-chamber window with the phased array probe placed over the patients’ point of maximal impact (PMI), with the patient in left lateral decubitus position.
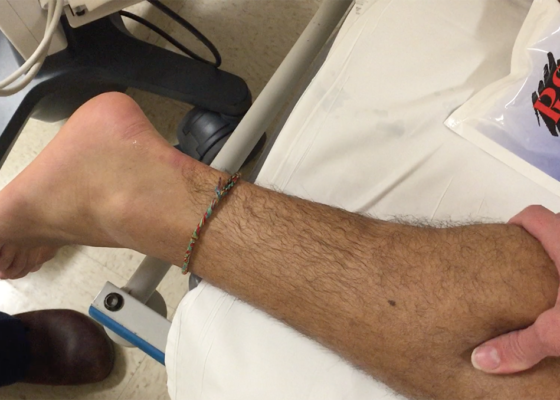
Thompson Test in Achilles Tendon Rupture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VC7SThe left Achilles tendon had a defect on palpation, while the right Achilles tendon was intact. When squeezing the right (unaffected) calf, the ankle spontaneously plantar flexed, indicating a negative (normal) Thompson test. Upon squeeze of the left (affected) calf, the ankle did not plantar flex, signifying a positive (abnormal) Thompson test. The diagnosis of left Achilles tendon rupture was confirmed intraoperatively one week later.
FAST Exam: Normal Suprapubic
Keywords: radiology, trauma, normal, suprapubic, FAST exam, videos, ultrasound, US
FAST Exam: Normal Morrison’s Pouch
Keywords: radiology, normal, renal, Morrison’s pouch, trauma, liver, ultrasound, video, FAST exam