Latest Articles
Residents Are Coming: A Faculty Development Curriculum to Prepare a Community Site For New Learners
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87D2NOur goal is to prepare community-based EM attendings to be outstanding educators to future residents by augmenting their knowledge of current educational practice and adult learning theory, literature review, and biostatistics.
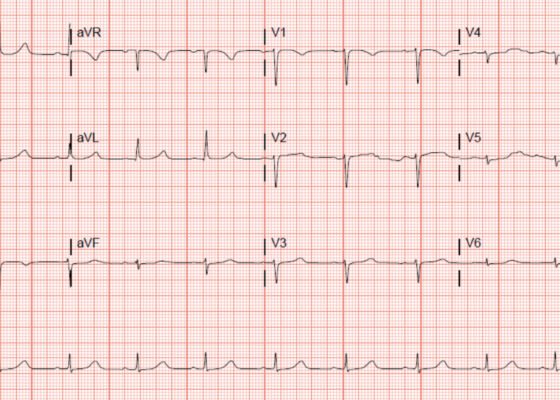
‘Cath’ It Before It’s Too Late: A Case Report of ECG Abnormalities Indicative of Acute Pathology Requiring Immediate Catheterization
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8HW7VA 12 lead ECG performed at the time of emergency department (ED) admission revealed regular sinus rhythm with noted T-wave inversion (blue arrows on Figure 1) in Lead aVL new when compared to an ECG performed a few months prior (see Figure 3). Two days later a second ECG was done when the patient developed acute chest pain while in the ICU (Figure 2) that showed persistent inversion in Lead aVL (blue arrows) as well as new J point deviation (JPD) in Leads II, aVF, V5 and V6; and new JPD in Leads V1 and V2 (green arrows) from her previous ECG while in the emergency department. These focal repolarization abnormalities did not qualify as an ST-elevation myocardial infarction by current guidelines.
Evaluation of ACE-inhibitor Induced Laryngeal Edema Using Fiberoptic Scope: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83P9TPhysical exam was initially significant for swelling isolated to the right sided cheek and upper lip. There was no edema to lower lip, uvular swelling, or swelling to the submandibular space. She was speaking full sentences and did not endorse any voice changes. Initial vital signs were as follows: BP 125/77, HR 74, RR 16, and oxygen saturation of 100% on room air. Approximately 40 minutes later, after 125 mg solumedrol intravenous (IV) and 50mg diphenhydramine by mouth, swelling had spread to the entire upper lip and the patient reported spreading to her jaw (Photo 1). Although no jaw or submandibular edema was appreciated on physical exam, a flexible fiberoptic laryngoscope was used to evaluate the patient’s airways given worsening symptoms. Viscous lidocaine was applied intranasally five minutes prior to the procedure. The patient was positioned in a seated position on the stretcher. A flexible fiberoptic laryngoscope was then inserted through the nares and advanced slowly. Laryngoscopy showed diffuse edema of the epiglottis, arytenoids, and ventricular folds (see photos 2-4). Vital signs and respiratory status remained stable both during and after the procedure.
A Case Report of May-Thurner Syndrome Identified on Abdominal Ultrasound
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8C64KThe patient initially received a venous doppler ultrasound that showed no evidence of a right or left femoropopliteal venous thrombus. Due to the high suspicion of a DVT given the symmetric swelling to the entire limb and acute onset of pain, a CTV was ordered. The transverse view of the CTV showed chronic thrombotic occlusion of the proximal left common iliac vein associated with compression from the right common iliac artery (figure 1, transverse image of CTA), as well as thrombotic occlusion of the left internal iliac vein tributary and corresponding left ascending lumbar vein. Given the previously mentioned clinical context, these features suggested the diagnosis of May-Thurner syndrome.
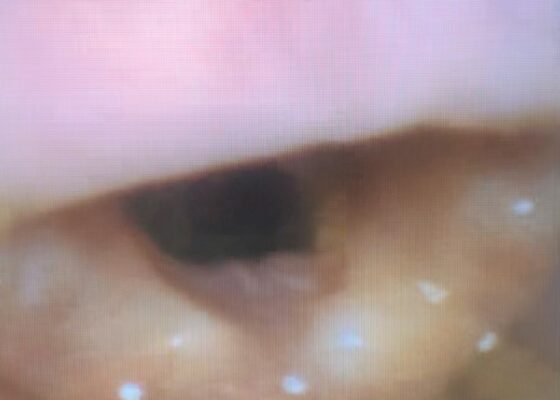
Vitreous Hemorrhage Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88D3BPoint of care ultrasound (POCUS) revealed hyperechoic material in the vitreous consistent with a vitreous hemorrhage. On the ultrasound images, there is visible hyperechoic debris seen floating in the vitreous as the patient moves his eye. Since the vitreous is typically anechoic (black) in color on ultrasound, turning up the gain on the ultrasound machine makes these findings easier to see and often highlights abnormalities, such as this hemorrhage (see annotated still).
High-Pressure Injection Injury to the Hand – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8D64WPlain radiographs of the left hand and forearm demonstrated extensive subcutaneous emphysema. The air can be seen as lucent striations tracking along the second and third fingers as well as along the dorsum of the hand and wrist. There is also diffuse soft tissue emphysema surrounding the metacarpophalangeal joints. Lab analysis did not show any significant acute abnormalities.
Management of Poisoned Patients: Implementing a Blended Toxicology Curriculum for Emergency Medicine Residents
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8C937The goal of this curriculum is to introduce EM residents to core toxicology concepts and to reinforce toxicology principles through a multimodal approach that leads to increased confidence in the management of poisoned patients on shift.
Peritonsillar Abscess Simulator: A Low-Cost, High-Fidelity Trainer
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J85M0BBy the end of this training session, learners will be able to: 1) locate the abscess, 2) perform needle aspiration, and 3) develop dexterity in maneuvering instruments in the small three-dimensional confines of the oral cavity without causing injury to local structures.
Breaking Bad News in the Emergency Department
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J81W7HAt the conclusion of these two simulation cases, learners will be able to 1) recognize signs of poor prognosis requiring emergent family notification, 2) take practical steps to contact family using available resources and personnel, 3) establish goals of care through effective family discussion, 4) use a structured approach, such as GRIEV_ING, to deliver bad news to patients’ families, and 5) name the advantages of family-witnessed resuscitation.