Latest Articles
Epilepsy Caused by Neurocysticercosis: A Case Report
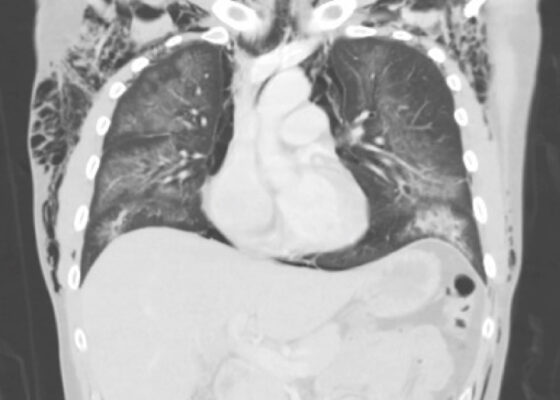
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J81P96In our patient, two lesions were most notable on CT in the frontal and occipital lobes. The lesion in the left frontal lobe (blue circle) was an approximately 1.5 centimeter (cm) rounded area with rim enhancement and surrounding hypodensity, consistent with vasogenic edema. A similar sized low-density area in the left occipital lobe (red circle) was noted, with increased peripheral density at the 3 o’clock position representing calcification. There were no areas of apparent hemorrhage or midline shift. The final radiology report concluded there were multiple cystic lesions, one with surrounding vasogenic edema in the left frontal lobe.
A Case of Community-Acquired Tuberculosis in an Infant Presenting with Pneumonia Refractory to Antibiotic Therapy
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8X07MChest radiographs during the initial presentation at seven weeks of life demonstrated right lower lobe (RLL) air space opacity on both PA and lateral views, compatible with pneumonia (referenced by yellow and green arrows, respectively). Repeat chest radiograph performed 12 days after the initial imaging revealed persistent right lower lobe opacity and right hilar fullness, seen as an opacified projection off of the mediastinal border as compared with the prior image, concerning for lymphadenopathy (designated by the aqua arrow). On the third presentation, computed tomography (CT) of the chest with intravenous contrast found persistent right lower lobe consolidation, innumerable 2-3 mm nodules, and surrounding ground glass opacities. This is best visualized as scattered areas of hyperdensity in the lung parenchyma. Axial images confirmed the presence of right hilar as well as subcarinal lymphadenopathy (indicated by white and pink arrows, respectively). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain with IV contrast was performed which showed a punctate focus of enhancement in the left precentral sulcus compatible with a tuberculoma (denoted with red arrow).
Electronic Cigarette or Vaping-Associated Lung Injury Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8S65PThe CT of the chest with contrast showed subcutaneous emphysema (green star), pneumomediastinum (yellow arrow), and pneumopericardium (purple asterix) without an identifiable tracheal tear. Extensive air was visualized as hypodense areas within the chest wall within the soft tissue. The image also detailed a hypodense area surrounding the heart consistent with pneumopericardium. No disruption of the trachea was present. Additionally, the CT of the chest also showed bilateral ground glass airspace opacities (red stars) with subpleural sparing that is consistent with EVALI findings.2,5 These specific findings have been seen in many of the EVALI cases.5 This image is interesting because there is extensive pneumomediastinum with no clearly identifiable cause. The imaging shows no esophageal or tracheal or lung injury, so it is important to note relevant information collected during interview regarding patient’s recent history of vaping THC, especially when establishing a differential diagnosis.
Case Report of a Tongue-Type Calcaneal Fracture
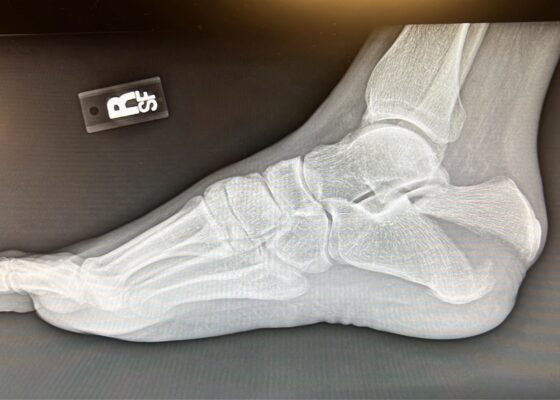
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NH11Examination of the right ankle demonstrated a large deformity of the superior talus with bruising and blanching of the overlying skin in the area of the Achilles tendon (see images 2,3). The remaining bones of the foot were not tender to palpation and the foot was neurovascularly intact throughout with only mild numbness in the area of the tented skin. Completing the trauma exam, the patient had no signs of head injury and no midline spinal tenderness to palpation. Inspection of the remaining long bones and joints showed no other injuries. There were mild skin scrapes on the right flank from the fall. X-rays of the right foot and ankle showed a longitudinal fracture of the calcaneal tuberosity from the articular surface to the posterior surface (see red outline) with extension into the subtalar joint (blue lines) and roughly 1.8 cm displacement between the fracture segments (yellow double arrow). These findings represented a tongue-type calcaneal bone fracture.
Use of An Ophthalmology Tutorial to Improve Resident Comfort with the Emergency Eye Exam
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86H0MBy the end of this small group didactic, learners will be able to: 1) demonstrate ability to focus on the various components of the slit lamp exam 2) demonstrate understanding of a systematic approach to the eye exam 3) demonstrate appropriate use of the Diaton, iCare, and Tonopen tonometers.
A Novel Module Based Method of Teaching Electrocardiogram Interpretation for Emergency Medicine Residents
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Z06JAfter completion of the module learners should be able to: 1) correctly recognize and identify ECG abnormalities including but not limited to abnormal or absent P waves, widened QRS intervals, ST elevations, abnormal QT intervals, and dysrhythmias that can lead to sudden cardiac death; and 2) synthesize findings into a succinct but accurate interpretation of the ECG findings.
A Model Curriculum for an Emergency Medicine Residency Rotation in Clinical Informatics
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82P9HThe aim of this curriculum is to teach informatics skills to emergency physicians to improve patient care and outcomes, utilize data, and develop projects to lead change.3 These goals will be achieved by providing a foundational informatics elective for EM residents that follows the delineation of practice for Clinical Informatics outlined by the American Medical Informatics Association (AMIA) and the American Board of Preventive Medicine (ABPM).
Respiratory Distress in the Pediatric ED: A Case-based Self-directed Learning Module
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8T64MEducational Objectives: By the end of this module, learners will be able to: 1) recognize the unique pathophysiology for respiratory distress in the pediatric population and formulate a broad differential; 2) understand the treatment principles for the most common causes of respiratory distress in children; 3) navigate and apply validated clinical decision-making tools for treatment of pediatric respiratory illnesses.
Methemoglobinemia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8PH1BAt the end of this simulation case, participants should be able to: 1) recognize shortness of breath, cyanosis and respiratory distress, and the difference between all of them based on the clinical presentation 2) identify the underlying cause of the condition by conducting a thorough history and physical 3) know how to identify and treat methemoglobinemia by ordering necessary labs and interventions and understand the pathophysiology leading to methemoglobinemia 4) recognize patient’s response to treatment and continue to reassess.
Torsade de Pointes Due to Hypokalemia and Hypomagnesemia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8JP8GBy the end of this simulation session, learners will be able to: 1) formulate appropriate work-up for altered mental status (AMS) 2) recognize hypokalemia and associated findings on ECG 3) address hypomagnesemia in a setting to hypokalemia 4) manage pulseless VT by following advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) 5) recognize and address TdP 6) provide care after return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) 7) consult intensivist and admit to intensive care unit (ICU).