Renal/Electrolytes
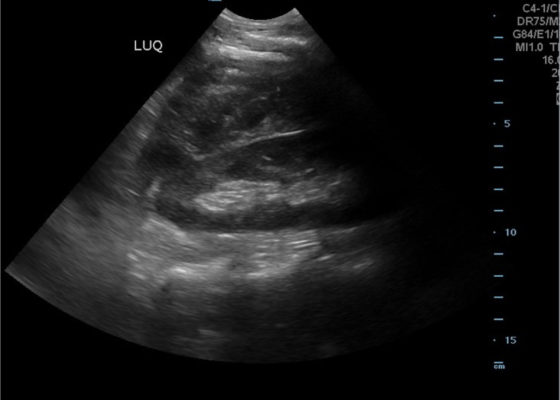
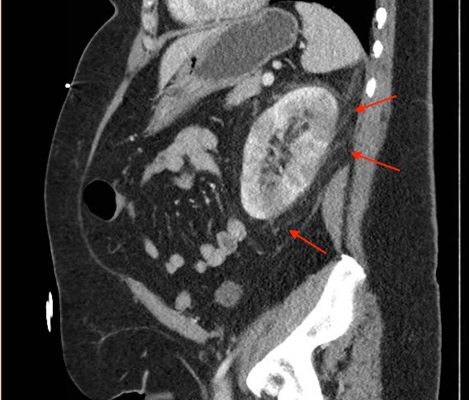
Hemorrhagic Renal Cyst
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8C92VBedside renal ultrasound demonstrated a right renal cyst with echogenic debris consistent with a hemorrhagic cyst (red arrow). In addition, a computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis revealed a 4mm non-obstructing right renal stone and bilateral renal cysts. The CT also confirmed the ultrasound finding of a right renal cyst with mild perinephric stranding possibly consistent with a hemorrhagic cyst.
FAST Exam to Diagnose Subcapsular Renal Hematoma
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NP8DA bedside point of care ultrasound FAST exam was performed revealing a left subcapsular renal hematoma. The hematoma was a non-compressing hematoma, evidenced by preserved renal contour with the hematoma labeled with a red H and the normal renal contour labeled with a green K. Additionally, cortical necrosis and ischemia can be characterized by a dark, hypoechogenic renal cortex on ultrasonography with a decrease in flow to the cortex on color doppler which was not seen on this patient, providing further evidence that the hematoma was non-compressing. The hematoma was concluded to be an acute process due to its hypoechoic appearance with some mixed ultrasonographic echoes caused by the early deposit of fibrin.
Erectile Dysfunction as a Presenting Symptom for Renal Cell Carcinoma
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8563BThe MRI showed extensive spondylotic changes suggestive of malignancy (red arrows) with severe spinal canal stenosis at the lumbar spine L3-L4 (purple arrows) level contributing to clumping of cauda equina nerve roots and severe bilateral neuroforaminal narrowing with diffuse disc bulges abutting the exiting nerve roots at multiple levels. Findings also showed a hypo-attenuated tumor (blue arrow) and hyper-attenuated loculated tumor (green arrow) consistent with renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
A Woman with Arm Spasms
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VP88The patient had a witnessed episode of isolated left upper extremity jerking, shown in the video, during which she was completely awake and conversant. Lab results were significant for serum glucose of 1167 mg/dL, no anion gap, and negative serum/urine ketones. She had a computed tomography (CT) of the head that did not show any acute pathology, and underwent a brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) without any signs of stroke or other pathology, shown below.
Computed Tomography and Ultrasound Diagnosis of Spontaneous Subcapsular Renal Hematoma
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8062DBedside ultrasound was performed and demonstrated a hypoechoic area within the left kidney (images not shown). The non-contrast computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis shows a significantly enlarged left kidney and a region of high-attenuation encapsulating the left kidney, concerning for acute hemorrhage.
Acute Pyelonephritis with Perinephric Stranding on CT
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BH0VA CT abdomen and pelvis with IV contrast showed neither nephrolithiasis nor diverticulitis, and instead showed heterogeneous enhancement of the left kidney with mild edematous enlargement and striated left nephrogram. Significant perinephric stranding (red arrows) was also noted and was consistent with severe acute pyelonephritis.
Hemodialysis in the Poisoned Patient
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88S68By the end of this cTBL, the learner will: 1) recognize laboratory abnormalities related to toxic alcohol ingestion; 2) calculate an anion gap and osmolal gap; 3) know the characteristics of drugs that are good candidates for HD; 4) discuss the management of patients with toxic alcohol ingestions; 5) discuss the management of patients with salicylate overdose; 6) know the indications for HD in patients with overdoses of antiepileptic drugs; 7) discuss the management of patients with lithium toxicity.
Renal Infarction from Type B Aortic Dissection
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8HG9GInitial abdominal images demonstrated a dissection flap; therefore, a CTA of the chest was also obtained. These images revealed a Stanford type B aortic dissection beginning just distal to the left subclavian artery and extending to the origin of the inferior mesenteric artery. The right renal artery arose from the true lumen of the dissection while the left renal artery arose from the false lumen. This case is interesting as imaging shows the lack of perfusion to the left kidney, residing in the retroperitoneum, which correlates with her non-descript abdominal and left flank pain.