Renal/Electrolytes
The EMazing Race: A Novel Gamified Board and Clinical Practice Review for Emergency Medicine Residents
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8.52075By the end of this 2-hour session, learners will demonstrate their knowledge on the following board-related emergency medicine topics: Ob/GYN – links to 13.7 Complications of Delivery in Core Model of EM 2022, Renal/GU – links to 15.0 Renal and Urogenital Disorders in Core Model of EM 2022 and Splinting – links to 18.1.8.2 Extremity bony trauma, fracture in Core Model of EM 2022.
Metastatic Calcinosis Cutis in the Emergency Department: A Case Report
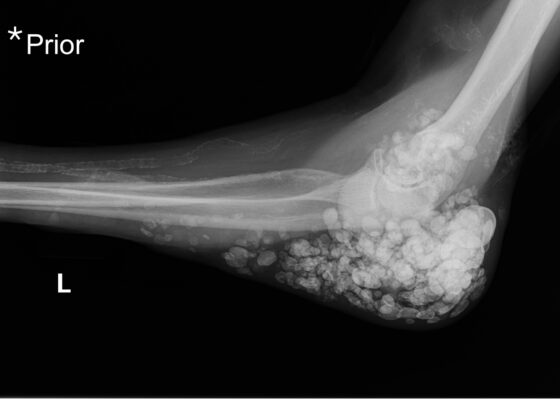
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87Q00X-ray imaging was obtained of the left elbow and showed soft tissue calcium deposits. Radiology stated, “massive periarticular calcinosis of renal failure obscures fine osseous detail. Several of the largest calcifications have decompressed since the prior exam and may contribute to the drainage observed clinically. Superimposed infection is not excluded.” X-rays with an asterisk are the comparison images from two months previous to the visit. Areas of decompression are highlighted in blue demonstrating that some of the larger calcified nodules are no longer present.
A Case Report of Calciphylaxis
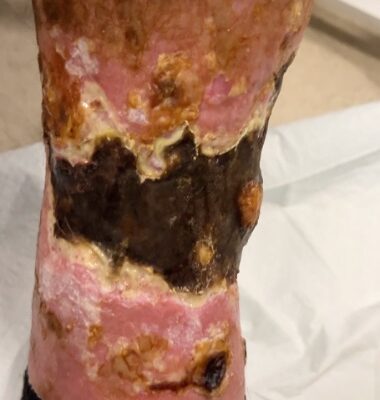
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KW8VOn arrival for this visit, the patient was nontoxic appearing with stable vital signs. The physical exam was notable for deep, ulcerated, bilateral anterior leg wounds with purulent drainage and large areas of eschar (see photographs).
A Patient with Generalized Weakness – A Case Report
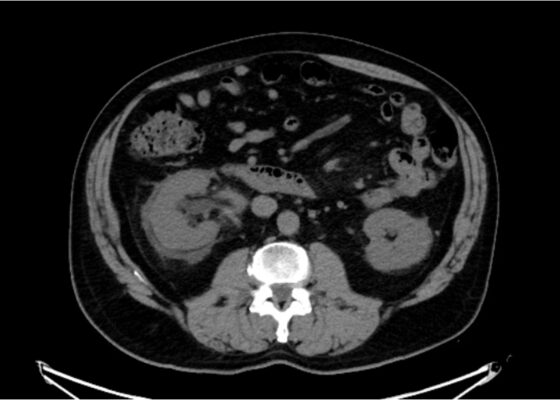
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8593CThe CT of the abdomen and pelvis showed evidence of a large subcapsular rim-enhancing fluid collection with multiple gas and air-fluid levels along the right kidney measuring 8 x 4 cm axially and 11 cm craniocaudally (blue outline) with mass effect on the right renal parenchyma (yellow outline). Another suspected fluid collection adjacent to the upper pole of the right kidney measuring 4 x 3.4 cm was noted (red outline). Bilateral pyelonephritis was suggested without hydronephrosis or nephrolithiasis. The findings suggested complicated pyelonephritis with emphysematous abscess and hematoma formation.
Case Report of a Pelvic Kidney with Ureteral Obstruction from Inguinal Hernia Entrapment and Concurrent Cryptorchid Testis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8F345The patient was afebrile with normal lactate and white blood cell count. Initial CT imaging showed an ectopic right pelvic kidney with entrapment of his right ureter within an indirect right inguinal hernia causing severe hydronephrosis (coronal: white arrow). Also discovered was an ovoid hypodensity in the right anterior pelvis consistent with right undescended testis (axial: orange arrow; coronal: green arrow) that was previously unknown to the patient, with a normal left scrotal testis (axial: red arrowhead; coronal: blue arrowhead). Other potential etiologies of the patient’s symptoms could include appendicitis or incarcerated inguinal hernia, though the imaging results and absence of systemic inflammatory response syndrome made these causes less likely.
Case Report of Unusual Facial Swelling in an 8-Month-Old
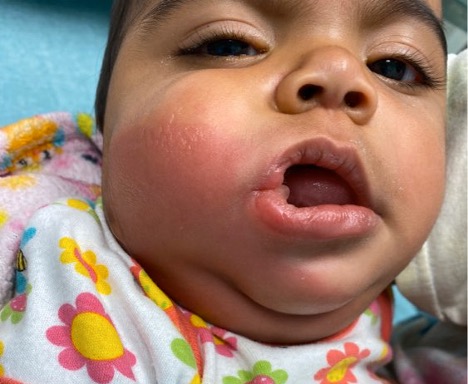
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8M06FFacial ultrasound revealed local inflammatory changes such as increased echogenicity and heterogeneity in the soft tissues of the right cheek, suggestive of soft tissue edema. There was evidence of a prominent right parotid gland with increased heterogeneity suggestive of a traumatic injury. Additionally, facial ultrasound demonstrated a 6mm ill-defined anechoic collection within the right cheek without increased doppler flow (green arrow), thought to represent a focal area of edema instead of an abscess.
Case Report: Not Your Typical Kidney Stone
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8GD2TThe CT scan demonstrates nephrolithiasis with associated forniceal rupture. Encircled in the yellow outline is fluid, demonstrating a forniceal rupture. The stone is in the proximal aspect of the ureter, as highlighted by the purple arrow.
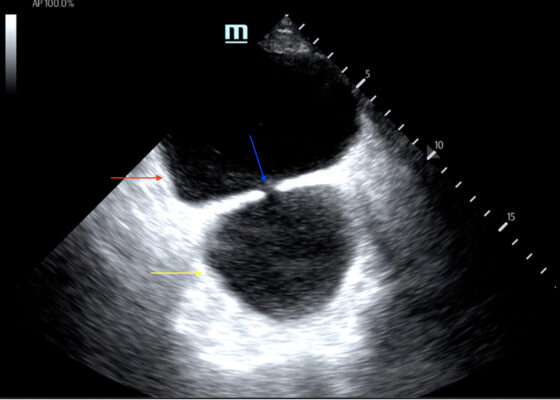
Bladder Diverticulum – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8635COn examination, the patient was alert and oriented but in mild distress. Suprapubic fullness was noted upon abdominal palpation. Point of care ultrasound of the bladder showed two enlarged “bladders” with a central communication. Bedside total bladder volume was measured to be 1288 cm3 (the top “bladder” was measured to be 1011 cm3, while the bottom “diverticulum” was measured to be 277 cm3) by ultrasound.
The POCUS stills of the patient’s bladder demonstrated the bladder (red arrow) and bladder diverticulum (yellow arrow) with a central communication (blue arrow) in the transverse and sagittal views.