Orthopedics
The EMazing Race: A Novel Gamified Board and Clinical Practice Review for Emergency Medicine Residents
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8.52075By the end of this 2-hour session, learners will demonstrate their knowledge on the following board-related emergency medicine topics: Ob/GYN – links to 13.7 Complications of Delivery in Core Model of EM 2022, Renal/GU – links to 15.0 Renal and Urogenital Disorders in Core Model of EM 2022 and Splinting – links to 18.1.8.2 Extremity bony trauma, fracture in Core Model of EM 2022.
A Comprehensive and Modality Diverse Cervical Spine and Back Musculoskeletal Physical Exam Curriculum for Medical Students
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8RQ0NBy the end of this session, students will be able to: 1) demonstrate how to properly perform a cervical spine and back physical exam, 2) understand the reasoning behind cervical spine and back PE maneuvers, 3) identify the proper technique and equipment to use for the cervical spine and back PE, 4) understand normal and abnormal findings in the cervical spine and back PE, 5) accurately record and report exam findings for the cervical spine and back PE.
Orthopaedic Surgery Didactic Session Improves Confidence in Distal Radius Fracture Management by Emergency Medicine Residents
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8K365By the end of this didactic session, learners should be able to: 1) assess DRF displacement on pre-reduction radiography and formulate reduction strategies, 2) perform a closed reduction of a DRF, 3) apply a safe and appropriate plaster splint to patient with a DRF and assess the patient’s neurovascular status, 4) assess DRF post-reduction radiography for relative fracture alignment, and 5) understand appropriate follow-up and necessary return precautions.
A Case Report of Lateral Subtalar Dislocation: Emergency Medicine Assessment, Management and Disposition
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8SS8PIn a lateral subtalar dislocation, the navicular bone (red bone in 3D anatomy image) and the calcaneus (yellow bone in 3D anatomy image) dislocate laterally in relation to the talus (lavender bone in 3D anatomy image). Plain film oblique and lateral X-rays demonstrate the initial dislocation (talus in red, navicular in blue). It is clear in the initial lateral view that there is loss of the talar/navicular articulation (noted by red arrow). The anterior-posterior x-ray is more challenging to discern the anatomy; however, the talus (red dot) is laterally displaced in comparison to the navicular (blue dot).
A Case Report of Acute Compartment Syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87061Inspection of the extremity revealed significant swelling with dark discoloration and multiple bullae (pre-operative photograph). Furthermore, notable swelling of the right foot was noted, which felt cold to palpation. Radiographs of pelvis, bilateral knees, tibia, fibula, and feet demonstrated no fractures or dislocations. The bilateral tibia and fibula X-ray revealed soft tissue swelling in the proximal legs, particularly evident in the right leg's AP view, which also showed numerous ovoid radiodensities in the anterior compartment, likely related to soft tissue injury. Post operative images are also provided demonstrating the patients’ four compartment fasciotomies which were loosely closed using staples.
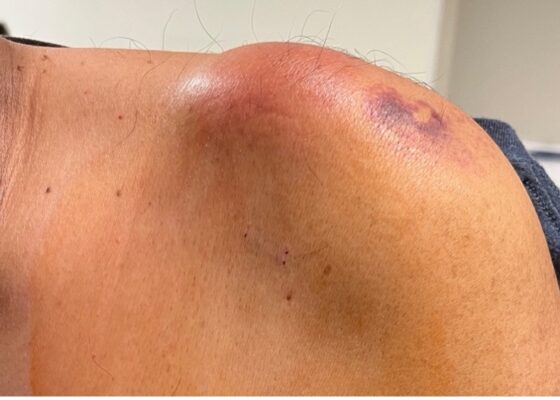
Septic Arthritis of the Acromioclavicular Joint: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VP9NMagnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with contrast was obtained of the shoulder and ankle, and results from both scans showed findings consistent with septic arthritis complicated by intraarticular abscesses. The MRI of the patient’s left acromioclavicular joint is shown as both a T1-weighted sequence in sagittal view and T2-weighted sequence in coronal view. The images show effusion (the dark fluid denoted by the red arrow) with an adjacent fluid collection (blue arrow). A T2-weighted MRI in coronal view of the patient’s right ankle showing multiple effusions (green arrows) and a fluid collection along the medial tibial cortex and subcutaneous tissues (yellow arrow).
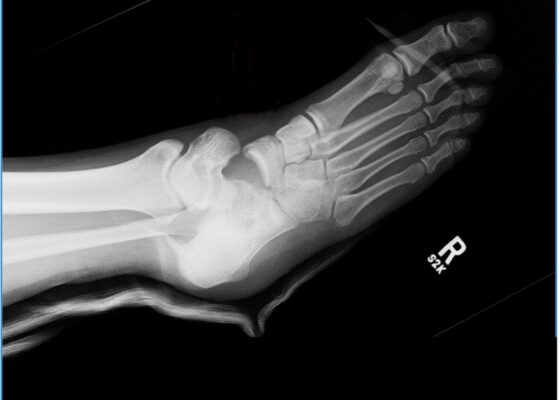
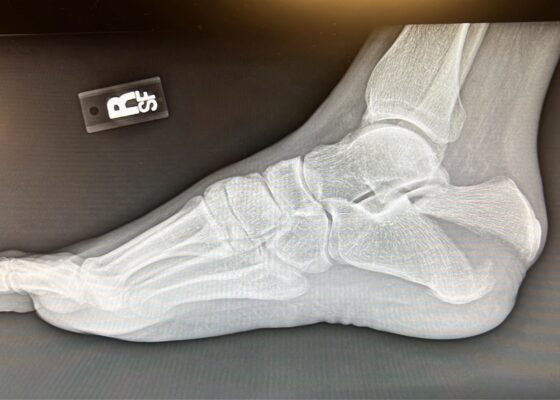
Case Report of a Tongue-Type Calcaneal Fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NH11Examination of the right ankle demonstrated a large deformity of the superior talus with bruising and blanching of the overlying skin in the area of the Achilles tendon (see images 2,3). The remaining bones of the foot were not tender to palpation and the foot was neurovascularly intact throughout with only mild numbness in the area of the tented skin. Completing the trauma exam, the patient had no signs of head injury and no midline spinal tenderness to palpation. Inspection of the remaining long bones and joints showed no other injuries. There were mild skin scrapes on the right flank from the fall. X-rays of the right foot and ankle showed a longitudinal fracture of the calcaneal tuberosity from the articular surface to the posterior surface (see red outline) with extension into the subtalar joint (blue lines) and roughly 1.8 cm displacement between the fracture segments (yellow double arrow). These findings represented a tongue-type calcaneal bone fracture.
High-Pressure Injection Injury to the Hand – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8D64WPlain radiographs of the left hand and forearm demonstrated extensive subcutaneous emphysema. The air can be seen as lucent striations tracking along the second and third fingers as well as along the dorsum of the hand and wrist. There is also diffuse soft tissue emphysema surrounding the metacarpophalangeal joints. Lab analysis did not show any significant acute abnormalities.