Endocrine
Case Report of a Patient Presenting with Nonketotic Hyperglycemia Hemichorea
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8.52115Laboratory tests indicated elevated blood glucose levels (198 mg/dL) with no urinary ketones, anion gap of 12, thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) of 12 UIU/ml, and an increased glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) of 14.9%. After initial stroke evaluation with neurology, imaging studies, including computed tomography (CT)/CT angiography (CTA) of the brain and neck, were unremarkable, ruling out structural lesions or acute stroke. Neurology recommended an MRI which showed T1 shortening within the left basal ganglia involving both the caudate nucleus and the lentiform nucleus. T1 shortening indicates changes in the tissue composition or structure that alters how the tissue responds to the MRI pulse, giving the tissue a brighter appearance on MRI (see white arrow).
A Cold Case: Myxedema Coma
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VM0JAt the conclusion of the simulation, the learner is expected to: 1) Recognize the key features on history and examination of a patient presenting in myxedema coma and initiate the appropriate workup and treatment, 2) Describe clinical features and management for a patient with myxedema coma, 3) Develop a differential diagnosis for a critically ill patient with altered mental status, 4) Discuss the management of myxedema coma in the ED, including treatments, appropriate consultation, and disposition.
Adolescent with Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Hypothermia and Pneumomediastinum
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8FP8JBy the end of the simulation, learners will be able to: 1) develop a differential diagnosis for an adolescent who presents obtunded with shortness of breath; 2) discuss the management of diabetic ketoacidosis; 3) discuss management of hypothermia in a pediatric patient; 4) discuss appropriate ventilator settings in a patient with diabetic ketoacidosis; and 5) demonstrate interpersonal communication with family, nursing, and consultants during high stress situations.
A Case Report of Glycogenic Hepatopathy
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8SQ0ZThe ultrasound images reveal hepatomegaly and an increased echogenicity of the liver parenchyma that is diffuse. The increased echogenicity can be best appreciated by a comparison to surrounding structures. It is important to note that the increased echogenicity is non-focal and consistent throughout the entire liver in multiple views. These findings can be consistent with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis as well as glycogenic hepatopathy.
A Case Report of a Large Goiter Resulting in Tracheal Deviation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J80645In the image, one can see significant tracheal deviation around the right side of the mass (black arrows). This degree of deviation would make ventilation in a paralyzed patient extremely difficult, if not impossible.
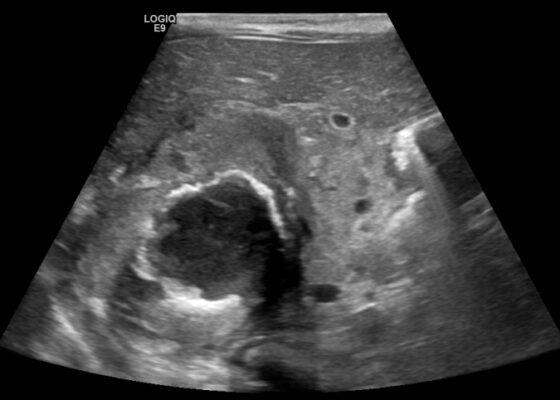
A Case Report of Neonatal Vomiting due to Adrenal Hemorrhage, Abscess and Pseudohypoaldosteronism
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QQ0BAn ultrasound (US) of the abdomen was obtained to evaluate for possible pyloric stenosis (see US transverse/dopper imaging). While imaging showed a normal pyloric channel, it revealed an unexpected finding: a complex cystic mass arising from the right adrenal gland (yellow outline), measuring 5.8 by 4.0 by 6.4 cm with calcifications peripherally and mass effect on the kidney without evidence of vascular flow (blue arrow). Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen/pelvis with IV contrast was subsequently obtained and measured the lesion as 2.8 by 4.6 by 4 cm without evidence of additional masses, lymphadenopathy or left adrenal gland abnormality (see CT axial, coronal, and sagittal imaging).
1›
Page 1 of 2