Cardiology/Vascular
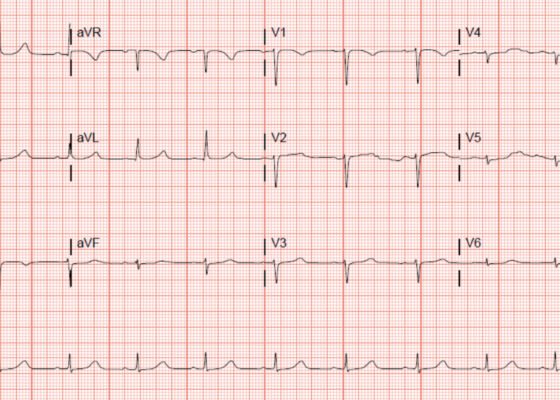
A Case Report of Subtle EKG Abnormalities in Acute Coronary Syndromes Indicative of Type One Myocardial Infarction
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8W06XThe ECG does show multiple subtle abnormalities that in conjunction with his symptoms and risk factors are concerning for ischemia and/or occlusion of the coronary artery vessel. 1) ST depression in aVL. Although slight, the ST segment is below the TP segment or isoelectric point (blue circles). 2) Focal hyper QT waves. The T-waves in II, III, AVF V2, V3, and V4 are hyper acute, namely peaked and tall in relationship to the QRS. These are best displayed in leads II, III, and AVF where the T-waves are taller than the QRS amplitude (vertical blue lines). 3) Straightening off the ST segment. Multiple leads display a straight ST segment namely aVL, III, AVF, and V2 (red lines). Of note, the length of the straight ST segment is greater than 1/4 the amplitude of the QRS (purple lines). 4) Although subtle, these abnormalities are focal in nature.
Aortic Dissection Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8964ZIn transverse view, point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) showed an anechoic circular true lumen (blue highlight) and half-circular anechoic false lumen (green highlight), separated by a near hyperechoic dissection flap (orange highlight) that pulsated with blood flow. When viewed in sagittal orientation, the anechoic true lumen (blue highlight) appears longitudinal, separated from the false lumen (green highlight) by a dissection flap (orange highlight). Stills showing the measurements of these dissections are also provided.
A Novel Module Based Method of Teaching Electrocardiogram Interpretation for Emergency Medicine Residents
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Z06JAfter completion of the module learners should be able to: 1) correctly recognize and identify ECG abnormalities including but not limited to abnormal or absent P waves, widened QRS intervals, ST elevations, abnormal QT intervals, and dysrhythmias that can lead to sudden cardiac death; and 2) synthesize findings into a succinct but accurate interpretation of the ECG findings.
Torsade de Pointes Due to Hypokalemia and Hypomagnesemia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8JP8GBy the end of this simulation session, learners will be able to: 1) formulate appropriate work-up for altered mental status (AMS) 2) recognize hypokalemia and associated findings on ECG 3) address hypomagnesemia in a setting to hypokalemia 4) manage pulseless VT by following advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) 5) recognize and address TdP 6) provide care after return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) 7) consult intensivist and admit to intensive care unit (ICU).
Inferior STEMI Electrocardiogram in a Young Postpartum Female with Sickle Cell Trait with Chest Pain – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KP95ECG shows evidence of ST segment elevation in the inferolateral leads with reciprocal change in a bigeminy pattern. The ECG pattern seen in this patient demonstrates ST elevations in the inferior leads (II, III, and avF) as well as the precordial leads V4-V6. Reciprocal changes can also be seen in leads I and avL. Though this STEMI pattern is typically associated with occlusion of the right coronary artery in 80% of cases, it may also be caused by occlusion of the left circumflex artery. This may explain this patient’s cardiac catheterization findings of vasospasm in the left circumflex coronary artery.
Aortic Dissection Presenting as a STEMI
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8W647At the conclusion of the simulation session or during the debriefing session, learners will be able to: 1) Verbalize the anatomical differences and management of Stanford type A and type B aortic dissections, 2) Describe physical exam findings that may be found with ascending aortic dissections, 3) Describe the various clinical manifestations of the propagation of aortic dissections, 4) Discuss the management of aortic dissection, including treatment and disposition.
‘Cath’ It Before It’s Too Late: A Case Report of ECG Abnormalities Indicative of Acute Pathology Requiring Immediate Catheterization
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8HW7VA 12 lead ECG performed at the time of emergency department (ED) admission revealed regular sinus rhythm with noted T-wave inversion (blue arrows on Figure 1) in Lead aVL new when compared to an ECG performed a few months prior (see Figure 3). Two days later a second ECG was done when the patient developed acute chest pain while in the ICU (Figure 2) that showed persistent inversion in Lead aVL (blue arrows) as well as new J point deviation (JPD) in Leads II, aVF, V5 and V6; and new JPD in Leads V1 and V2 (green arrows) from her previous ECG while in the emergency department. These focal repolarization abnormalities did not qualify as an ST-elevation myocardial infarction by current guidelines.