Abdominal/Gastroenterology
Point of Care Ultrasound as a Diagnostic Tool to Detect Small Bowel Obstruction in the Emergency Department: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8XD1GThe ultrasound findings suggestive of small bowel obstruction (SBO) are typically visualized in video; however, certain still images can also demonstrate SBO including greater than three dilated loops of small bowel (>2.5 cm), thickened-walled bowel (>3 mm), visualization of plicae circulares, and extraluminal fluid caused by inflammatory changes along the bowel wall, which are all highly suggestive of SBO.3
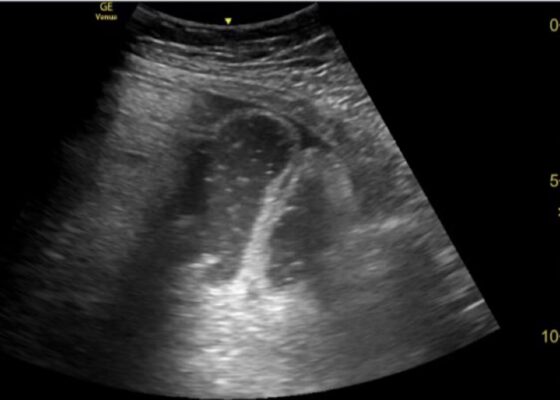
In this patient’s case, we were able to visualize several dilated loops of small bowel (red arrow) with oscillating intraluminal contents known as “Whirl Sign.” Additionally, we were able to visualize extraluminal fluid, demonstrated as an anechoic triangular-shaped collection. The characteristic shape of this triangular shaped collection of fluid is known as a “Tanga Sign,” given its name due to way it looks similar to the lower half of a bikini (blue arrow). Tanga sign can occur when the loops of dilated bowel appear prominent in contrast to the inflammatory extraluminal fluid in an SBO. These ultrasound findings were highly concerning for SBO which was later confirmed on CT imaging of the abdomen, which demonstrated SBO with a transition point in the left lower quadrant.
A Case Report on Detecting Porcelain Gallbladder form Wall-Echo-Shadow Sign on Point-of-Care Ultrasound
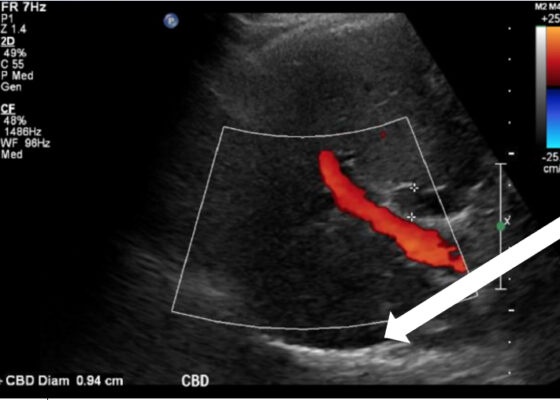
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8164GPoint-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) was performed by the emergency physician. Gallbladder ultrasound (US) should be performed using a curvilinear probe. If the patient’s body habitus does not allow for the use of a curvilinear probe, a phased array probe may be used. To find the gallbladder with ultrasonography, two approaches are commonly used. Many physicians prefer the “subcostal sweep” in which the probe is placed on the xiphoid process in a sagittal plane and swept along the inferior costal margin until the gallbladder is visualized. If this does not adequately locate the gallbladder, the “X minus 7” approach may be used. In this approach, the probe is placed on the xiphoid (X) process in a transverse view and moved 7 centimeters (minus 7) to the patient’s right. This technique is useful for patients with a larger body habitus. If the gallbladder is still not visualized, placing the patient in left lateral decubitus position or asking them to take a deep breath and hold may help the ultrasonographer locate the gallbladder. The US revealed mild hepatic biliary duct dilation with cholelithiasis and sludge, but no additional evidence to suggest cholecystitis. The US image showed a dilated common bile duct at 0.94 cm and calcifications. Visualization of the gallbladder wall is essential in differentiating between a positive wall-echo-shadow (WES) sign and a porcelain gallbladder. While a hypoechoic gallbladder wall is indicative of a WES sign, a hyperechoic wall layer will indicate a calcified gallbladder wall, suggesting a porcelain gallbladder. In image 1, the hyperechoic gallbladder wall can be visualized (white arrow), suggesting the presence of porcelain gallbladder and distinguishing it from a positive WES sign.
Vomiting in Pediatric Patients
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8P363By the end of this TBL session, learners should be able to: 1) Identify red flag symptoms that should prompt referral for urgent intervention by GI or surgical specialists; 2) recognize how chronicity of the vomiting can alter the differential diagnosis; 3) describe the varying pathways that can cause nausea and vomiting; 4) determine the necessity of imaging tests to confirm and possibly treat various causes of vomiting; 5) interpret imaging studies associated with specific causes of vomiting.
A Case Report of Ogilvie’s Syndrome in a 58-year-old Quadriplegic
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82922Plain radiograph of the patient's abdomen revealed a gaseous distention of the colon. This is demonstrated as noted in the abdominal x-ray as gaseous distention, most notably in the large bowel (arrows) including the rectal region (large circle). Follow up computed tomography (CT) scan affirmed severe pancolonic gaseous distention measuring up to 11.2 cm, compatible with colonic pseudo-obstruction as noted by the large red arrows. No anatomical lesion or mechanical obstruction was observed, as well as no evidence of malignancy or other acute process.
Cecal Volvulus Diagnosed with a Whirl Sign: A Case Report
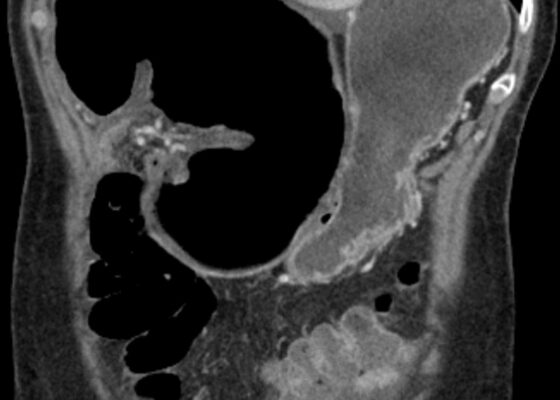
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8XM05The CT image demonstrates a “whirl sign” (red arrow) which is indicative of a volvulus. This image occurs when bowel, mesentery and vasculature rotate around a transition point causing an image similar to a hurricane on a weather map. When seen on a CT scan, a whirl sign suggests a high likelihood of either a closed loop bowel obstruction or volvulus in the cecum, sigmoid or midgut. In any of the cases, seeing a whirl sign strongly increases the need for emergent surgical management.
Is an X-ray a Useful Test for Esophageal Food Boluses? A Case Report
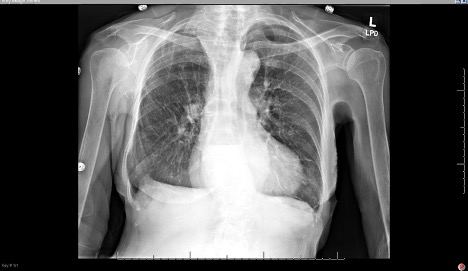
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Q639The plain film radiograph of the chest demonstrated a fluid level (yellow arrow) in the distal esophagus with dilation of the esophagus proximal to that point (blue line). Neither of these findings were present on the previous visit.
Loose PEG Tube Leading to Peristomal Leakage and Peritonitis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8HS7TFrontal chest X-ray showed a large radiolucent area (pink highlighted area) underneath the diaphragm (yellow line) and on top of the liver (blue highlighted area) and spleen (green highlighted area) suggestive of pneumoperitoneum possibly caused by gastrointestinal perforation. This large radiolucent area can also be seen underneath the diaphragm in the lateral view chest X-ray. Computed tomography (CT) was not performed due to his physical exam findings and the significant positive findings on chest X-ray. Surgery was consulted and patient was taken emergently to the operating room.
Hemorrhagic Renal Cyst
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8C92VBedside renal ultrasound demonstrated a right renal cyst with echogenic debris consistent with a hemorrhagic cyst (red arrow). In addition, a computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis revealed a 4mm non-obstructing right renal stone and bilateral renal cysts. The CT also confirmed the ultrasound finding of a right renal cyst with mild perinephric stranding possibly consistent with a hemorrhagic cyst.