Abdominal/Gastroenterology
Case Report of Incarcerated Gastric Volvulus and Splenic Herniation in Undiagnosed Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia in an Infant
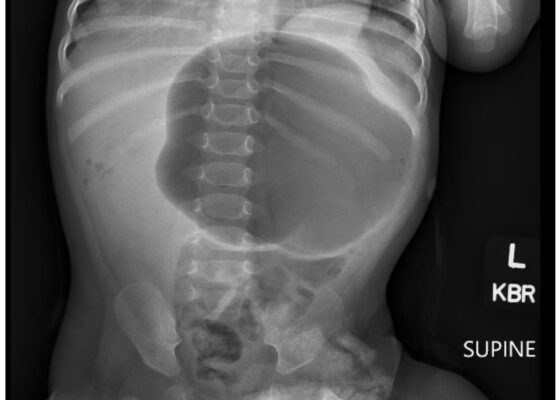
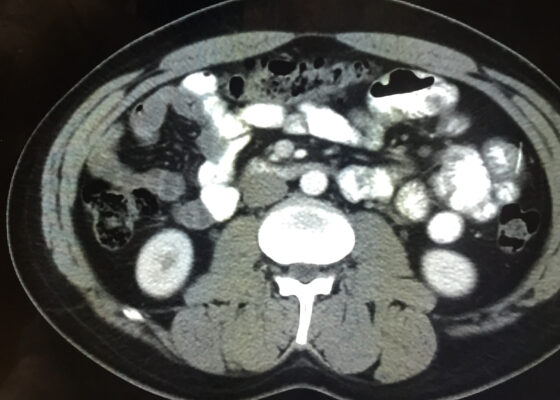
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VD27An upper gastrointestinal series (UGI) showed an enteric tube with its tip in the stomach and side-port in the esophagus. There was a large amount of air in the stomach and a small volume of scattered distal bowel gas. The tip of an enteric tube was seen in the stomach (red arrow). Contrast partially filled the stomach, and the greater curvature was visualized superior to the lesser curvature in the left upper quadrant (blue arrow). The body of the stomach was herniated into the right chest through a Bochdalek hernia (blue star). There was a large amount of air in the stomach and a small volume of scattered distal bowel gas. These findings were consistent with mesenteroaxial gastric volvulus.
Case Report: Iatrogenic Bowel Perforation Following Dental Procedure
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8CD38The patient’s abdominal CT demonstrated a metallic foreign body in the left side of the abdomen within the small bowel, without surrounding induration or abscess. Radiology questioned whether the metallic foreign object perforated the bowel. Seen in the cross-sectional CT image, there is a hyperdense linear structure transversing the small intestinal wall, given that a portion of the structure was located outside of the lumen of the bowel.
A Case Report of Hydropic Gallbladder Presenting as Right Lower Quadrant Abdominal Pain
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8DD26Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast was ordered, and general surgery was consulted for the initial working diagnosis of acute appendicitis. However, the CT scan resulted with findings of a markedly distended gallbladder measuring approximately 14.5 x 4 centimeters (cm) with marked gallbladder wall thickening (magenta) and pericholecystic fat stranding (cyan). The appendix was not dilated and had no inflammatory changes or edema. Follow-up right upper quadrant ultrasound confirmed the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis.
A Simulation and Small-Group Pediatric Emergency Medicine Course for Generalist Healthcare Providers: Gastrointestinal and Nutrition Emergencies
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8WH2KThe aim of this curriculum is to increase learners’ proficiency in identifying and stabilizing acutely ill pediatric patients with gastrointestinal medical or surgical disease or complications of malnutrition. This module focuses on the diagnosis and management of gastroenteritis, acute bowel obstruction, and deficiencies of feeding and nutrition. The target audience for this curriculum is generalist physicians and nurses in limited-resource settings.
Telescoping into Adulthood: A Case Report of Intussusception in an Adult Patient
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Q06CComputed tomography imaging of the abdomen and pelvis with intravenous and oral contrasts was obtained. In the axial view, one will see a concentric ring formed by layers of bowel, mesenteric vessels, and fat (red arrow and circle); this is the equivalent of the ultrasonographic “target sign.” The inner ring (blue arrow) represents the lead point causing telescoping of the bowel. One can see that the proximal bowel is dilated (yellow arrow). In the coronal view, one can see an obstructive mass, also known as the lead point (red arrow), located in the lumen of the descending colon. Located proximal to the lead point are dilated loops of bowel with edematous changes and fat stranding (pink circle). The proximal portion of the bowel will take on a concentric appearance with the telescoping loop of bowel.