Posts by JETem
The Clue is in the Eyes. A Case Report of Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8DP9MThere was no appreciable esotropia or exotropia noted on straight gaze (yellow arrows). On extraocular muscle examination, patient was noted to have a complete left medial rectus palsy consistent with a left internuclear ophthalmoplegia (red arrow). This was evidence by both eyes easily gazing left (green arrows); however, with rightward gaze, her left eye failed to gaze past midline (red arrow).
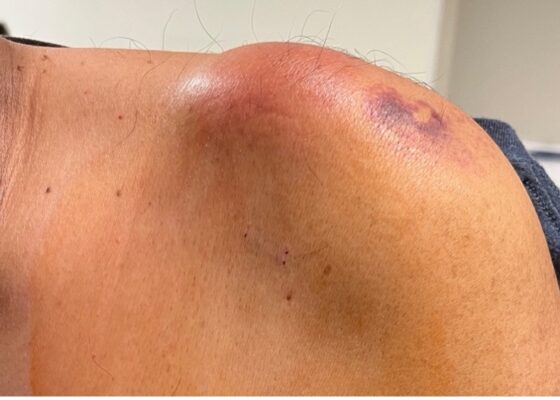
Septic Arthritis of the Acromioclavicular Joint: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VP9NMagnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with contrast was obtained of the shoulder and ankle, and results from both scans showed findings consistent with septic arthritis complicated by intraarticular abscesses. The MRI of the patient’s left acromioclavicular joint is shown as both a T1-weighted sequence in sagittal view and T2-weighted sequence in coronal view. The images show effusion (the dark fluid denoted by the red arrow) with an adjacent fluid collection (blue arrow). A T2-weighted MRI in coronal view of the patient’s right ankle showing multiple effusions (green arrows) and a fluid collection along the medial tibial cortex and subcutaneous tissues (yellow arrow).
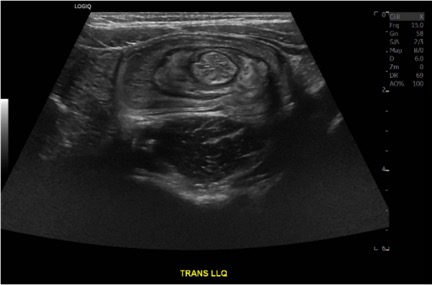
Case Report of a Child with Colocolic Intussusception with a Primary Lead Point
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8564QOn the initial ED visit, an abdominal ultrasound (US) was ordered which showed the classic intussusception finding of a target sign (yellow arrow), or concentric rings of telescoped bowel, on the transverse view of the left lower quadrant (LLQ).
Low-Cost Fishhook Removal Simulation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Q64PThe goal of this small group session is to fill the gap in training on fishhook injuries. At the end of the session participants should be able to describe the parts of a fishhook, as well as demonstrate and have increased confidence in performing multiple fishhook removal techniques.
Enneagram in EM
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8ZM0GBy the end of this session, the learner will be able to: 1) Self-identify with a primary enneagram personality type. 2) List the fears, desires, and motivations of the enneagram type. 3) Describe struggles in interacting with other disparate enneagram types. 4) Discuss strategies for success in facing conflict and interacting with other team members.
Adolescent with Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Hypothermia and Pneumomediastinum
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8FP8JBy the end of the simulation, learners will be able to: 1) develop a differential diagnosis for an adolescent who presents obtunded with shortness of breath; 2) discuss the management of diabetic ketoacidosis; 3) discuss management of hypothermia in a pediatric patient; 4) discuss appropriate ventilator settings in a patient with diabetic ketoacidosis; and 5) demonstrate interpersonal communication with family, nursing, and consultants during high stress situations.
Ventricular Tachycardia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KD2RAt the conclusion of the simulation session, learners will be able to: 1) identify the different etiologies of VT, including structural heart disease, acute ischemia, and acquired or congenital QT syndrome; 2) describe confounding factors of VT, such as electrolyte abnormalities and sympathetic surge; 3) describe how to troubleshoot an unsuccessful synchronized cardioversion, including checking equipment connections, increasing delivered energy, and changing pad placement; 4) compare and contrast treatments of VT based on suspected underlying etiology; 5) describe reasons to activate the cardiac catheterization lab other than occlusive myocardial infarction; and 6) identify appropriate disposition of the patient to the cardiac catheterization lab.
Inhalational Injury Secondary to House Fire
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TW7NAt the conclusion of the simulation session, learners will be able to: 1) recognize the indications for intubation in a thermal burn/inhalation injury patient; 2) develop a systematic approach to an inhalational injury airway; and 3) recognize indications for transfer to burn center.