Orthopedics
Introducing point-of-care ultrasound through competency-based simulation education using a fractured chicken bone model
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8GG95To introduce medical students to PoCUS with an inexpensive, reproducible, and educationally effective model using fractured chicken bones set in gelatin, and to assess medical students’ abilities to identify simulated long-bone fractures using PoCUS.
Supracondylar Fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8492PHistory of present illness: A 15-year-old male presented to the emergency department with right elbow pain after falling off a skateboard. The patient denied a decrease in strength or sensation but did endorse paresthesias to his hand. On exam, the patient had an obvious deformity of his right elbow with tenderness to palpation and decreased range of motion at the
Galeazzi Fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8HS39The X-ray showed an acute comminuted fracture of the distal diaphysis of the radius with disruption of the distal radioulnar joint, consistent with a Galeazzi fracture. The patient was then splinted and taken for operative reduction and internal fixation the following day.
A Formalized Three-Year Emergency Medicine Residency Musculoskeletal Emergencies Curriculum
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8RG6HResident learners will master the diagnosis and management of emergent musculoskeletal conditions including fractures/dislocations, soft tissue injuries, compartment syndrome, joint complaints, infections, and complex injuries.
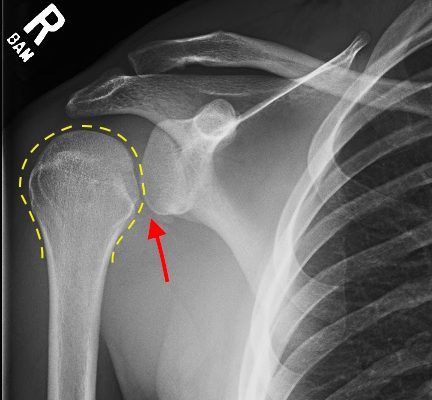
Irreducible Traumatic Posterior Shoulder Dislocation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8V884Radiographs demonstrated posterior displacement of the humeral head on the “Y” view (see white arrow) and widening of the glenohumeral joint space on anterior-posterior view (see red arrow). The findings were consistent with posterior dislocation and a Hill-Sachs type deformity. Sedation was performed and reduction was attempted using external rotation, traction counter-traction. An immediate “pop” was felt during the procedure. Post-procedure radiographs revealed a persistent posterior subluxation with interlocking at posterior glenoid. CT revealed posterior dislocation with acute depressed impaction deformity medial to the biceps groove with the humeral head perched on the posterior glenoid, interlocked at reverse Hill-Sachs deformity (see blue arrow).
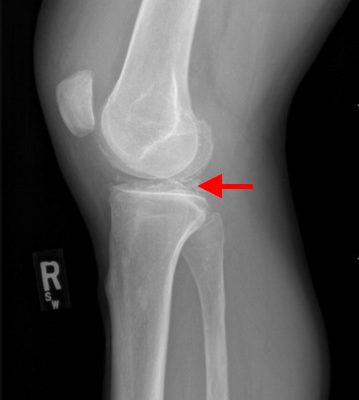
Pseudogout and Calcium Pyrophosphate Disease
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QG66Radiographs of the knee showed multiple radio-dense lines paralleling the articular surface (see red arrows) consistent with calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition within the joint often seen in calcium pyrophosphate disease (CPPD) also known as pseudogout.
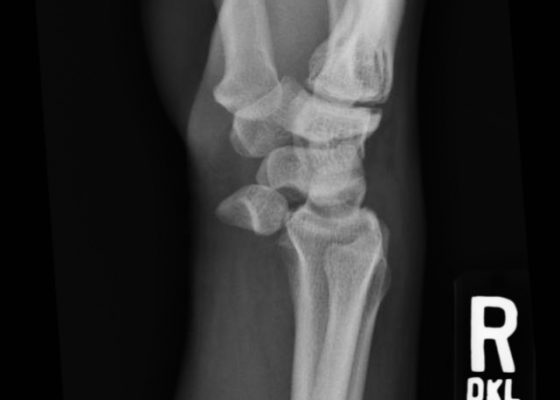
Lunate Dislocation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86K56Plain film of the right wrist showed the classic “spilled teacup” consistent with a lunate dislocation. There is a loss of the normal articulation between the distal radius and lunate.
Pediatric Supracondylar Fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8T88TPlain film radiography showed a displaced supracondylar fracture with disrupted anterior and posterior periostea, consistent with a type 3 supracondylar fracture.