Ophthalmology
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension and Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter
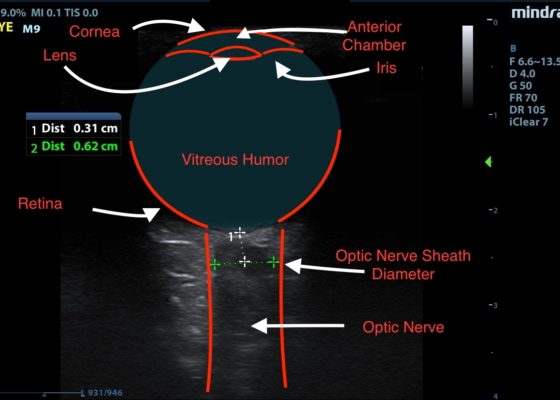
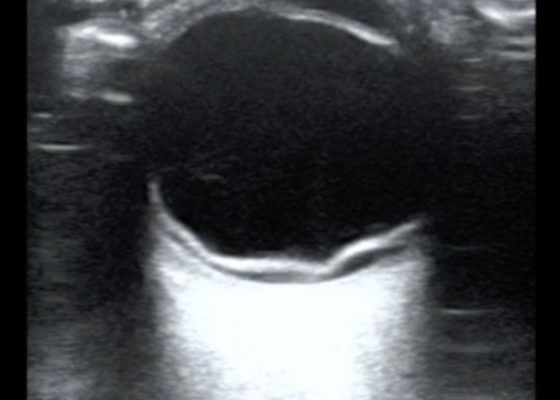
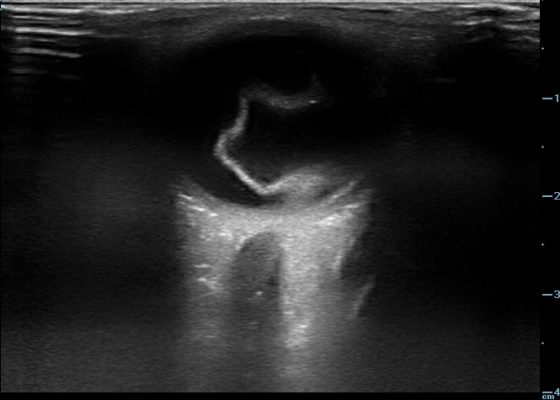
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J84631Optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) was measured via ultrasound with diameter 5.7mm on left and 6.2mm on right. In order to measure ONSD via optic ultrasound the high-frequency linear array probe (7.5-10-MHz or higher) is utilized in B-mode. The patient is positioned supine and an occlusive dressing, such as Tegaderm, is placed over a closed eyelid with copious conductive gel on top of the dressing. Being careful not to put pressure on the globe, an axial cross-sectional image of the globe is obtained. As demonstrated in the image “annotated left eye ONSD pre-lumbar puncture,” there are two main anechoic areas of the globe, the anterior chamber and the vitreous humor. These anechoic structures are separated by the hyperechoic iris, which surfaces the hyper-echoic-lined lens. At the back of the vitreous humor is the retina, which leads posteriorly into the optic nerve. The optic nerve is the hypoechoic structure posterior to the retina and surrounded by the hyperechoic subarachnoid space, which is encased by the hypoechoic dura mater. The outer edge of the hypoechoic dura matter is where the ONSD is measured.1 The user applies calipers to measure 3mm perpendicularly behind the retina along the hypoechoic optic nerve, and at this level the transverse dimensions of the ONSD are measured using calipers as shown in the images.Computed tomography (CT) of the head was performed and showed no abnormalities. Lumbar puncture was performed in left lateral decubitus position revealing elevated opening pressure of 29cm H2O. Thirty-five mL of clear cerebral spinal fluid was drained and was negative for all infectious studies. Optic nerve sheath diameter was again measured post-lumbar puncture with diameters 5.4mm on left and 5.4mm on right.
Open Globe with Intraocular Foreign Body
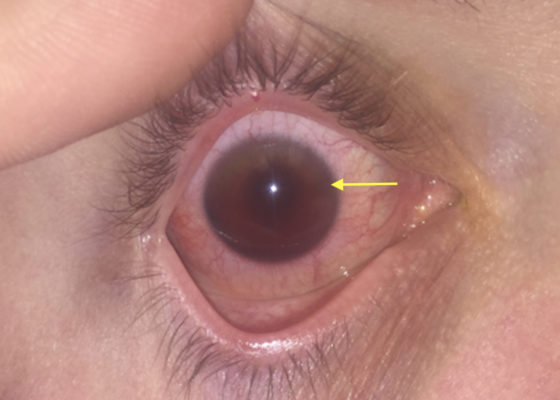
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8S348On physical exam, his extraocular movements were intact. The right anterior chamber appeared cloudy, particularly nasal to the pupil. The conjunctiva of the right eye was injected. The right pupil was 3 mm and sluggishly reactive and appeared slightly irregular (see yellow arrow). Of note, the right eye also had a 1 mm hypopyon, indicating inflammation of the anterior chamber, which was visible on slit lamp examination (not pictured). There was no fluorescein uptake or Seidel sign. His visual acuity was 20/60 OD (right eye) and 20/20 OS (left eye).
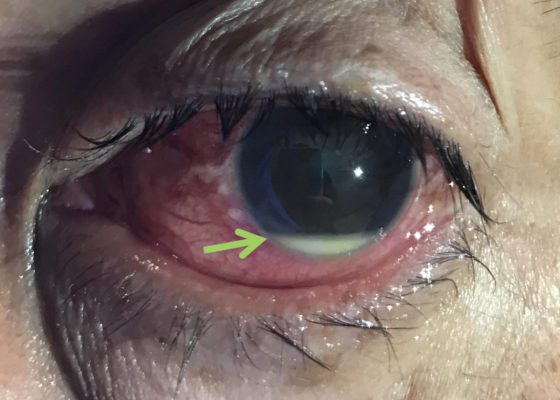
Hypopyon
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8N92BPhysical examination of the left eye revealed a hypopyon (green arrow) – which is a layered white to yellow sediment in front of the inferior aspect of the iris associated with scleral injection and chemosis. Extraocular movements were intact bilaterally and pain did not worsen with extraocular movement. The pupil was poorly reactive to direct light and only hand movement could be perceived. The intraocular pressure was 14 mmHg. Slit lamp exam demonstrated a dense cataract. Bedside ocular ultrasound demonstrated vitreous opacities concerning for possible intraocular foreign bodies.
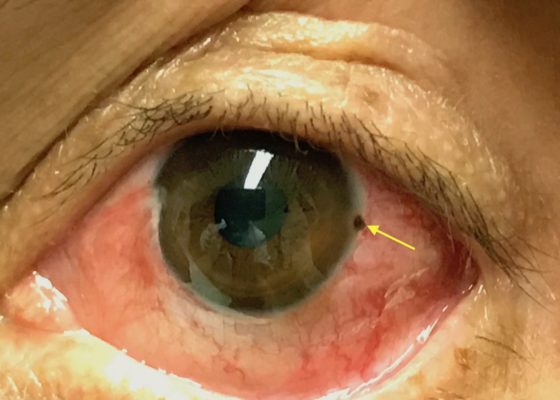
Corneal Rust Ring
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8X067The photograph reveals a limbic metallic foreign body with a surrounding corneal rust ring (arrow) in the three o’clock position of the left cornea.
Bedside Ultrasound of Retinal Detachment in a 19-year-old
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J80W6TThe ocular point of care ultrasound (POCUS) utilizing a high frequency linear probe shows a retinal detachment (RD) with a thick, hyperechoic undulating membrane in the vitreous humor that is anchored at the ora serrata anteriorly and the optic disc posteriorly. Note that the retina is detached all the way to the optic disc making it "mac off." The macula, and more specifically the fovea, is located in the central retina and contains a high concentration of cone photoreceptors responsible for central, high resolution, color vision. In a "mac on" RD, the retina detaches in the periphery but remains intact centrally. This is an ophthalmologic emergency and timely diagnosis and intervention can be vision saving. This patient also has evidence of a posterior vitreous hemorrhage which has a characteristic swirling appearance with kinetic exam on real-time imaging. The detached vitreous body is not as well defined and is not anchored posteriorly to the optic disc.
Traumatic Hyphema
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Z04SUpon initial evaluation, the patient had an obvious hyphema in the right eye with associated conjunctival injection. Initially, the bleeding in the anterior chamber was cloudy just above the level of the pupil (yellow arrow), appearing to possibly be a grade II hyphema. There were no other signs of trauma to the eye under Wood’s lamp examination with fluorescein staining. The globe was intact. Intraocular pressure in the affected eye was 19 mmHg and 15 mmHg in the unaffected eye. Extraocular movements were full and intact. The pupil was 4 mm round and reactive to direct and consensual light. Visual acuity was greater than 20/200 in the affected eye compared to 20/25 in the unaffected eye. After an observation period of two hours, with the patient remaining upright, the hyphema had settled down to a rim in the lower anterior chamber (green arrow), a grade I hyphema.
Retinal Detachment
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8204QBedside ocular ultrasound revealed a serpentine, hyperechoic membrane that appeared tethered to the optic disc posteriorly with hyperechoic material underneath. These findings are consistent with retinal detachment (RD) and associated retinal hemorrhage.
Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88H07Physical exam was significant for an erythematous maculopapular rash in the right ophthalmic nerve (V1) region, a crusted vesicle at the right upper eyelid, and surrounding eyelid edema. Visual acuity remained at baseline and intraocular pressure was within normal limits. External slit lamp exam with fluorescein staining was remarkable for pseudodendrites in the inferior-temporal cornea approximately 1.5 mm from the limbus. Ophthalmology was consulted and completed an in-depth evaluation of the corneal lesions. They found no evidence of anterior chamber reaction and performed a complete dilated fundus examination which demonstrated no retinal involvement. The patient was then discharged on acyclovir and erythromycin ointment with close follow-up.