ENT
Sialadenitis
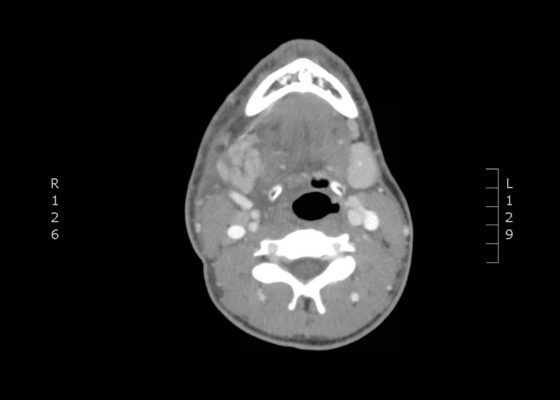
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NH0NThe computed tomography (CT) scan demonstrates prominent enlargement and heterogeneous enhancement of the right submandibular gland (single large arrow) compatible with sialadenitis. There is no evidence of a sialolith or obstruction on the CT. There is associated edema (two small arrows) of the right submandibular space, parapharyngeal space and anterior right neck with partial effacement of the right vallecula and right pyriform sinus.
An Unusual Case of Pharyngitis: Herpes Zoster of Cranial Nerves 9, 10, C2, C3 Mimicking a Tumor
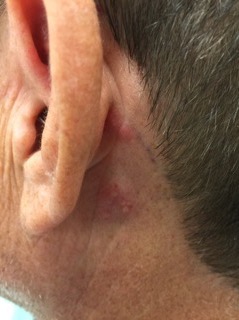
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8B05KOn exam, the patient was sitting upright while holding an emesis basin filled with saliva. His voice was noticeably hoarse. Examination of the head and neck revealed vesicular eruptions on the left scalp in the V1 dermatome and on the left mastoid process (Images 1 and 2). Physical exam also shows vesicular eruptions on the left posterior oropharynx that did not cross midline (Image 3).
Ramsay Hunt Syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J85S7QLeft-sided cranial nerve VII palsy with flattened forehead creases, inability to keep the left eye open, and drooping of the corner of mouth. Vesicular lesions were found in and posterior to the left ear in a unilateral, dermatomal distribution.
A Case of Otomastoiditis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8RK89The patient underwent computed tomography (CT) of the head which revealed opacification of the left middle ear (red arrow) and mastoid air cells (red circles). Additionally, there was thickening of the soft tissues of the external auditory canal (blue arrowhead), likely reflecting concurrent otitis externa. Based on the imaging, he was admitted for findings consistent with acute otomastoiditis.
A Sublingual Mass in a 5-Year-Old Male
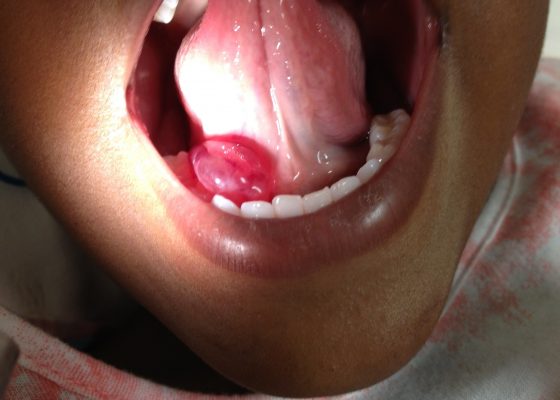
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8H622Oral ranula. On oral inspection he had a 3 x 1.5 cm, soft, non-tender, mobile, cystic, sublingual mass on the right aspect of the floor of his mouth that did not move with swallowing (Image 1). There was mild associated submandibular swelling on the right side of his face.
Novel Emergency Medicine Curriculum Utilizing Self-Directed Learning and the Flipped Classroom Method: Head, Eyes, Ears, Nose and Throat Emergencies Small Group Module
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8PW5NWe aim to teach the presentation and management of HEENT emergencies through the creation of a flipped classroom design. This unique, innovative curriculum utilizes resources chosen by education faculty and resident learners, study questions, real-life experiences, and small group discussions in place of traditional lectures. In doing so, a goal of the curriculum is to encourage self-directed learning, improve understanding and knowledge retention, and improve the educational experience of our residents.
Bedside Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Peritonsillar Abscess
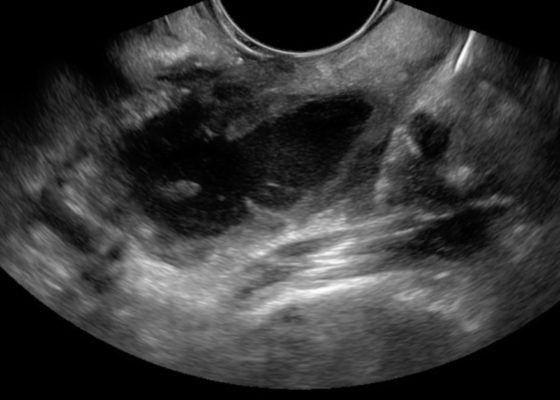
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8N33NThe first video is an intraoral ultrasound using the high frequency endocavitary probe demonstrating an anechoic fluid collection adjacent to the patient’s enlarged left tonsil. The second video shows real-time ultrasound-guided successful drainage of the PTA.
Oropharynx Ulceration
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87W60The photograph demonstrates an area of ulcerative tissue at the left palatine tonsil without surrounding erythema or purulent drainage. The computed tomography (CT) scan shows a large ulceration of the left soft palate and palatine tonsil (red arrow). There is no evidence of skull base osteomyelitis. There is suppurative lymphadenopathy with partial left jugular vein compression due to mass effect (yellow highlight). There is mild nasopharyngeal airway narrowing with architectural distortion (blue arrow), but no other evidence of airway obstruction.