Abdominal/Gastroenterology
An Appy That Needs Epi: An Atypical Presentation of Anaphylaxis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J80H14At the conclusion of the simulation, learners will be able to: 1) demonstrate ability to efficiently review patient records to optimize patient care and identify relevant details to current presentation, 2) rapidly assess a patient when there is a change in clinical status, 3) recognize the need to start resuscitative fluids for undifferentiated hypotension, 4) identify anaphylaxis, 5) demonstrate the medical management of anaphylaxis, 6) utilize the I-PASS framework to communicate with the inpatient team during the transition of care.
Case Report of a Child with Colocolic Intussusception with a Primary Lead Point
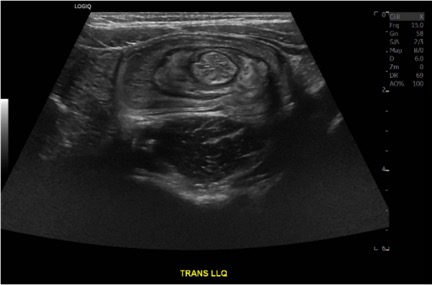
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8564QOn the initial ED visit, an abdominal ultrasound (US) was ordered which showed the classic intussusception finding of a target sign (yellow arrow), or concentric rings of telescoped bowel, on the transverse view of the left lower quadrant (LLQ).
Point-Of-Care Ultrasound Use for Detection of Multiple Metallic Foreign Body Ingestion in the Pediatric Emergency Department: A Case Report
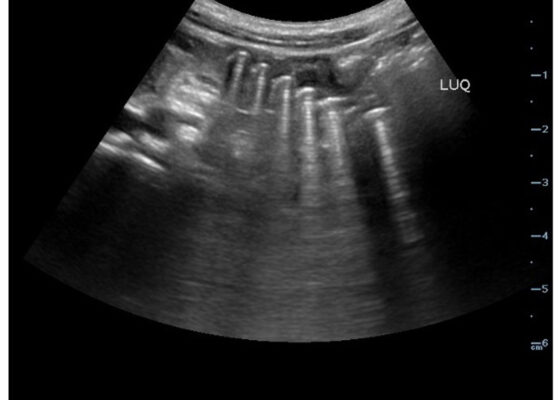
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83D2DBedside POCUS was performed on the patient’s abdomen using the curvilinear probe. The left upper quadrant POCUS image demonstrates multiple hyperechoic spherical objects with shadowing and reverberation artifacts concerning multiple foreign body ingestions. Though the patient and mother initially denied knowledge of foreign body ingestion, on repeated questioning after POCUS findings, the patient admitted to his mother that he ate the spherical magnets he received for his birthday about one week ago. The patient swallowed these over the course of two days. The presence of multiple radiopaque foreign bodies was confirmed with an abdominal X-ray.
Imaging Findings of Small Bowel – Diverticulitis: A Case Report
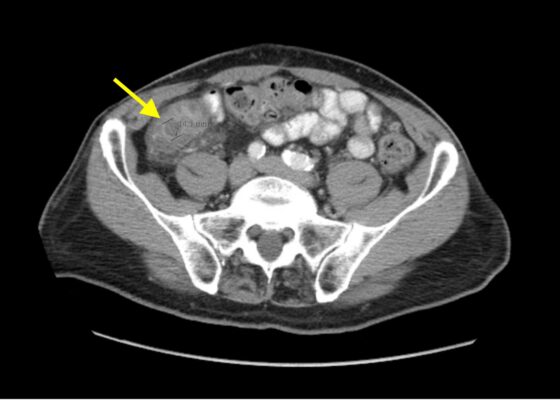
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8F078Bedside ultrasound was performed and showed thickened bowel wall (orange marker), fat enhancement (green marker), and phlegmonous structure with central echogenicity (yellow marker). Imaging of the abdomen and pelvis with CT showed marked wall thickening and inflammatory change involving a 7.0cm segment of the distal/terminal ileum suspicious for severe ileitis with phlegmon and microabscess on the coronal image (yellow arrow). Additonally, the transverse images show a small rim-enhancing focus within this region of inflammation measuring up to 1.4cm which could represent microabscess (yellow arrow). Diagnosis of diverticulitis by ultrasound is made by identifying the following findings: colon wall thicker than 5mm, fat enhancement, evidence of abscess, visualized diverticuli, air artifacts suggesting diverticuli, and tenderness with compression of the probe.6 Diagnosis of diverticulitis by CT is made by identifying the following findings: colonic wall thickening, pericolic fat stranding, abscess formation and enhancement of the colonic wall. Often, these signs are associated with an identifiable inflamed diverticulum.7
Mushroom for Improvement Case Report: The Importance of Involving Mycologists
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8ZW7WThe mushroom displayed here is large and lacks any gills. Small puffball mushrooms can resemble young immature button top Amanita type mushrooms. Opening the Amanita mushroom should reveal apparent gills and quickly differentiate the two- -the puffball mushroom should have a white interior without gills.
Massive Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8W93WBy the end of this simulation, learners will be able to: 1) manage a hypotensive patient with syncope and hematemesis, 2) pharmacologically manage an acute UGIB addressing the various causes, 3) recognize worsening clinical status and intervene by performing difficult airway management, 4) place a gastroesophageal balloon tamponade device.
Case Report: It’s a Small Whirl Afterall
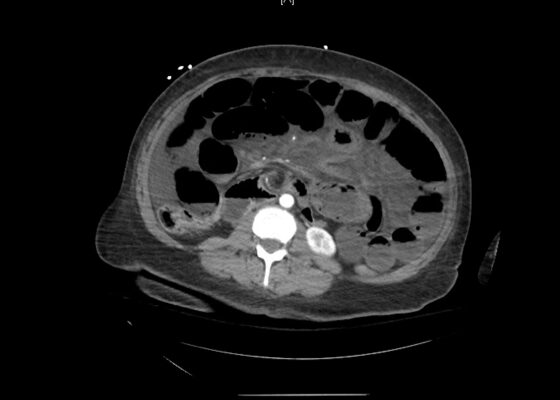
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83S8GThe CT imaging of the abdomen and pelvis demonstrated multiple loops of dilated small bowel with a whirl sign (red arrow) within the mid abdomen and a transition point (green arrow), suspicious for closed loop bowel obstruction and internal hernia.
Escape the EM Boards: Interactive Virtual Escape Room for GI Board Review
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8H63FBy the end of this didactic activity, learners will be able to: 1) identify causes of upper gastrointestinal bleeding; 2) recall test-taking buzzwords for infectious causes of diarrhea; 2) acknowledge the correct hepatitis B titers that correspond with various clinical scenarios; 3) describe the management for alkali caustic ingestions; 4) determine the components of Maddrey Discriminant Function Score, Charcot’s triad, Ranson’s Criteria for Pancreatitis, and Glasgow-Blatchford Score; 5) diagnose specific gastrointestinal diseases from a clinical description; 6) choose the correct gastrointestinal diagnosis based on clinical image findings; 7) demonstrate teamwork in solving problems.