Latest Articles
A Pediatric Emergency Medicine Refresher Course for Generalist Healthcare Providers in Belize: Respiratory Emergencies
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J84063This curriculum presents a refresher course in recognizing and stabilizing pediatric acute respiratory complaints for generalist healthcare providers practicing in LMICs. Our goal is to implement this curriculum in the small LMIC of Belize. This module focuses on common respiratory complaints, including asthma, bronchiolitis, pneumonia and acute airway management.
Point of Care Ultrasound as a Diagnostic Tool to Detect Small Bowel Obstruction in the Emergency Department: A Case Report
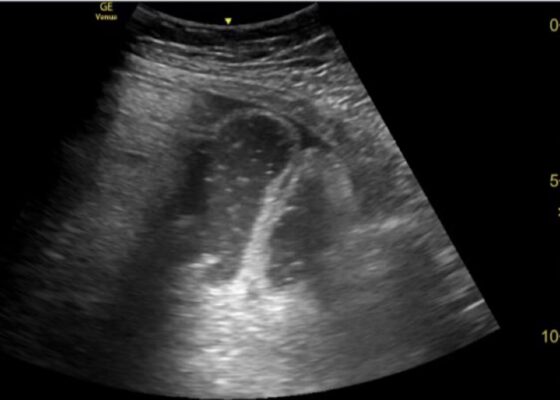
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8XD1GThe ultrasound findings suggestive of small bowel obstruction (SBO) are typically visualized in video; however, certain still images can also demonstrate SBO including greater than three dilated loops of small bowel (>2.5 cm), thickened-walled bowel (>3 mm), visualization of plicae circulares, and extraluminal fluid caused by inflammatory changes along the bowel wall, which are all highly suggestive of SBO.3
In this patient’s case, we were able to visualize several dilated loops of small bowel (red arrow) with oscillating intraluminal contents known as “Whirl Sign.” Additionally, we were able to visualize extraluminal fluid, demonstrated as an anechoic triangular-shaped collection. The characteristic shape of this triangular shaped collection of fluid is known as a “Tanga Sign,” given its name due to way it looks similar to the lower half of a bikini (blue arrow). Tanga sign can occur when the loops of dilated bowel appear prominent in contrast to the inflammatory extraluminal fluid in an SBO. These ultrasound findings were highly concerning for SBO which was later confirmed on CT imaging of the abdomen, which demonstrated SBO with a transition point in the left lower quadrant.
Case Report: Altered with PRES
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NW73On vitals, the patient was found to be consistently hypertensive to the 230s/160s. Point-of-care glucose was within normal limits. Noncontrast CT imaging of the head revealed no acute intracranial hemorrhage or evidence of ischemic stroke, but was remarkable for areas of biparietal subcortical low-attenuation (white arrows), concerning for PRES. Patient subsequently underwent CT angiogram imaging of the head with perfusion which revealed no large vessel occlusion.
A Case Report of Cardiac Tamponade
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8J644The patient was in noticeable respiratory distress and had oxygen saturation of 94% on room air. Bilateral jugular venous distention with severe right supraclavicular lymphadenopathy and diffuse bilateral wheezing was present. Although muffled heart sounds and hypotension are part of Beck’s Triad, these were not present in this case. Electrocardiogram obtained on arrival showed a sinus tachycardia with low-voltage QRS complexes and electrical alternans. Low voltage QRS can be seen on the ECG provided and is demonstrated by the low amplitude of the QRS complexes seen on all the leads. Electrical alternans may have an alternating axis or amplitudes of the QRS complex. Alternating axis is best visualized in V4-V6 on this ECG while alternating amplitudes are seen throughout the rest of the ECG. Computed tomography angiogram (CTA) of the chest revealed a large pericardial effusion with bilateral pulmonary emboli and a right upper lobe mass. A bedside transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) was then performed and confirmed the large effusion, but also showed right ventricular collapse during diastole, indicative of cardiac tamponade.
A Different Type of Tension Headache: A Case Report of Traumatic Tension Pneumocephalus
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8DH0GCT head without contrast demonstrated a minimally displaced fracture of the frontal sinuses at the midline underlying his known laceration that involved the anterior and posterior tables of the calvarium. This is seen on the sagittal view and indicated by the blue arrow. There was a small volume of underlying subarachnoid hemorrhage along the falx. There was also extensive pneumocephalus most pronounced along the bilateral anterior frontal convexity associated with the frontal sinus fracture, seen on the axial image and indicated by the red arrow. This pattern of air is commonly referred to as the “Mount Fuji” sign.6 Other intracranial air can also be seen on the sagittal image and is indicated by the white arrow.
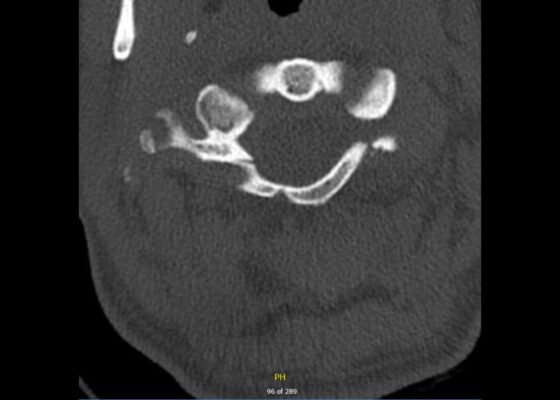
Jefferson Fracture and the Classification System for Atlas Fractures, A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88P9CComputed tomography (CT) revealed a burst fracture (Jefferson) of the anterior arch (white arrows) and of the posterior arch (yellow arrows) of the first cervical vertebrae (C1). There was also a fracture of the right lateral mass (blue arrow) of C1 with mild lateral subluxation of the lateral masses (curved arrows).
Using Point-of-Care Ultrasound to Expedite Diagnosis of Necrotizing Fasciitis: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J85051A consultative scrotal ultrasound was performed, which was read as showing a small right hydrocele, small bilateral scrotal pearls, and normal-appearing testes. Although present, there was no mention of subcutaneous air suggestive of NF, seen in figure 1 as punctate hyperechoic foci (arrowhead) with ring-down artifact known as dirty shadowing (arrow). Also, subcutaneous thickening (asterisk) and free fluid (arrow) were seen as shown in figure 2, although their clinical relevance was not recognized in the radiologist's final report. Figure 3 shows an abdominal and pelvic CT that re-demonstrates subcutaneous air in the scrotum and lower abdomen (arrow) as well as fascial thickening of the perineum and free intra-abdominal air. After these images, the patient was transferred to our hospital for further management. Almost immediately after the patient's arrival, POCUS was employed. As seen in figures 4, we were able to identify in just a few minutes extensive subcutaneous air accompanied by dirty shadowing, as well as re-demonstration of subcutaneous thickening, fluid collections, and a right hydrocele. Even without the outside hospital's CT, the sonographic findings were highly suggestive for the diagnosis of NF of the perineum, also known as Fournier’s gangrene.
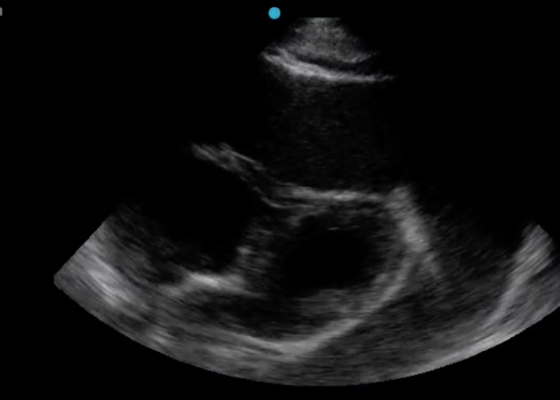
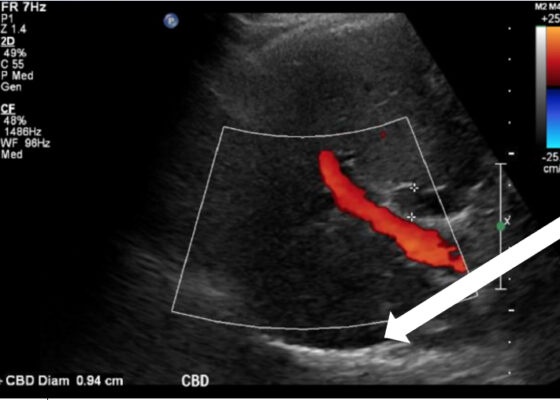
A Case Report on Detecting Porcelain Gallbladder form Wall-Echo-Shadow Sign on Point-of-Care Ultrasound
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8164GPoint-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) was performed by the emergency physician. Gallbladder ultrasound (US) should be performed using a curvilinear probe. If the patient’s body habitus does not allow for the use of a curvilinear probe, a phased array probe may be used. To find the gallbladder with ultrasonography, two approaches are commonly used. Many physicians prefer the “subcostal sweep” in which the probe is placed on the xiphoid process in a sagittal plane and swept along the inferior costal margin until the gallbladder is visualized. If this does not adequately locate the gallbladder, the “X minus 7” approach may be used. In this approach, the probe is placed on the xiphoid (X) process in a transverse view and moved 7 centimeters (minus 7) to the patient’s right. This technique is useful for patients with a larger body habitus. If the gallbladder is still not visualized, placing the patient in left lateral decubitus position or asking them to take a deep breath and hold may help the ultrasonographer locate the gallbladder. The US revealed mild hepatic biliary duct dilation with cholelithiasis and sludge, but no additional evidence to suggest cholecystitis. The US image showed a dilated common bile duct at 0.94 cm and calcifications. Visualization of the gallbladder wall is essential in differentiating between a positive wall-echo-shadow (WES) sign and a porcelain gallbladder. While a hypoechoic gallbladder wall is indicative of a WES sign, a hyperechoic wall layer will indicate a calcified gallbladder wall, suggesting a porcelain gallbladder. In image 1, the hyperechoic gallbladder wall can be visualized (white arrow), suggesting the presence of porcelain gallbladder and distinguishing it from a positive WES sign.
Auricular Perichondritis after a “High Ear Piercing:” A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8WH16On physical examination, there was erythema, swelling, warmth, and general exquisite tenderness of the superior aspect of the left pinna (the outer ear) but excluding the ear canal, lobe, tragus, and crus. There was no facial involvement. There was no fluctuance about the ear and no drainage of fluid. The preauricular lymph nodes were enlarged and tender, but the anterior cervical lymph nodes were not tender. There was no mastoid tenderness, protrusion of the ear, or interruption of the postauricular crease.
An Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia Elective for Emergency Medicine Residents
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TP9BABSTRACT: Audience: This ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia elective is designed for emergency medicine residents. Length of Curriculum: The proposed length of this curriculum is over one week. Introduction: Ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia (UGRA) is a useful tool in the emergency department (ED) for managing painful conditions, and many programs have identified that these are useful skills for emergency providers; however, only about