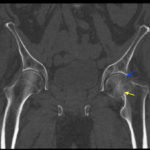
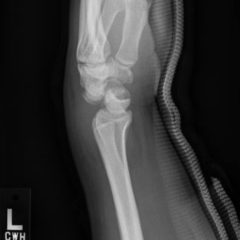
Femoral Neck Fracture
History of present illness:
A 74-year-old male presented to the emergency department with left hip pain after falling off his bicycle. Pain is 3/10 in severity and exacerbated by movement. Patient denied head trauma. Exam showed left hip tenderness, 3/5 left lower extremity strength secondary to pain, and 5/5 right lower extremity strength. Sensation and pulses were intact in bilateral lower extremities. Left hip X-ray and pelvic CT revealed comminuted, impacted transcervical and subcapital fracture of the left femoral neck.
Significant findings:
In the anteroposterior view bilateral hip x-ray, there is an evident loss of Shenton’s line on the left (red line) when compared to the normal right (white line), indicative of a fracture in the left femoral neck. This correlates with findings seen on pelvic CT, which reveals both a subcapital fracture (blue arrow) and transcervical fracture (yellow arrow). The neck of the femur is displaced superiorly relative to the head of the femur while the head of the femur remains in its anatomical position within the acetabulum.
Discussion:
Femoral neck fractures are one of the most common types of hip fractures, accounting for 49.4% of all hip fractures.1 Diagnosing a femoral neck fracture can be made with plain x-ray, CT, or MRI. Plain film radiographs have been found to be at least 90% sensitive for hip fractures CT’s have been found to be 87%-100% sensitive and 100% specific for occult hip fractures in which plain radiographs were read as negative, but the patient still complained of hip pain Although MRI is currently the gold standard for detecting occult hip fractures (sensitivity and specificity = 100%), given MRI’s limited accessibility in the ED as well as the high sensitivity and specificity of CT scans for occult hip fractures, it is generally recommended to obtain CT scans for patients with suspected occult hip fractures as a first-line investigation
Topics:
Shenton’s line, hip fracture, transcervical fracture, subcapital fracture, pelvis CT, hip x-ray, trauma, comminuted fracture, impacted fracture, femoral neck fracture, orthopedics.
References:
- Karagas MR, Lu-Yao GL, Barrett JA, Beach ML, Baron, JA. Heterogeneity of hip fracture: age, race, sex, and geographic patterns of femoral neck and trochanteric fractures among the US elderly. Am J Epidemiol. 1996;143:677-682.
- Dominguez S, Liu P, Roberts C, Mandell M, Richman PB. Prevalence of traumatic hip and pelvic fractures in patients with suspected hip fracture and negative initial standard radiographs – a study of emergency department patients. Acad Emerg Med. 2005;2:366-369. doi: 10.1197/j.aem.2004.10.024
- Thomas RW, Williams HL, Carpenter EC, Lyons K. The validity of investigating occult hip fractures using multidetector CT. Br J Radiol. 2016;89(1060):20150250.doi: 10.1259/bjr.20150250
- Haubro M, Stougaard C, Torfing T, Overgaard S. Sensitivity and specificity of CT- and MRI-scanning in evaluation of occult fracture of the proximal femur. Injury. 2015;46:1557-1561.doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2015.05.006
- Verbeeten KM, Hermann KL, Hasselqvist M, et al.The advantages of MRI in the detection of occult hip fractures. Eur Radiol. 2005;15:165-169. doi: 10.1007/s00330-004-2421-2
- Rehman H, Clement RG, Perks F, White TO. Imaging of occult hip fractures: CT or MRI? Injury. 2016;47:1297-1301. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2016.02.020