Trauma
Simulated Mass Casualty Incident Triage Exercise for Training Medical Personnel
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82H1RBy the end of this exercise, learners should be able to (1) recite the basic START patient categories (2) discuss the physical exam signs associated with each START category, (3) assign roles to medical providers in a mass casualty scenario, (4) accurately categorize patients into triage categories: green, yellow, red, and black, and (5) manage limited resources when demand exceeds availability.
Adult Clavicular Fracture Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8FM0TThe patient's chest and clavicular radiographs showed a comminuted displaced acute fracture of the right mid-clavicle (green, blue, yellow). The clavicular fracture was also visible on the chest computed tomography (CT). The remainder of his trauma workup was negative for acute findings.
Case Report of Distal Radioulnar Joint and Posterior Elbow Dislocation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J89S6KRadiographs of the left elbow and wrist were obtained. Left elbow radiographs showed simple posterolateral dislocation of the olecranon (red) without fracture of the olecranon (red) or trochlea (blue). Left wrist lateral radiographs demonstrated DRUJ dislocation with dorsal displacement of the distal ulna (green) without fracture or widening of the radioulnar joint (purple). Post-reduction radiographs demonstrated appropriate alignment of the elbow with the trochlea seated in the olecranon and improved alignment of the DRUJ.
A Case Report of Epidural Hematoma After Traumatic Brain Injury
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8R059Non-contrast CT head demonstrated a right sided EDH (red arrow) with overlying scalp hematoma, left-sided subdural hematoma (blue arrow), and bilateral subarachnoid hemorrhages. No skull fractures were noted.
Traumatic Diaphragmatic Rupture – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8G64HChest X-ray showed an elevated left hemi-diaphragm with superior displacement of a portion of intra-abdominal contents presumed to be the stomach (green arrowheads) with associated rightward mediastinal shift (yellow arrows). The diagnosis was confirmed by CT. Computed tomography imaging of the chest showed a large, left diaphragmatic defect measuring approximately 5.5 cm with herniation of the upper half of the stomach through the defect. The fundus of the stomach (blue arrow) herniated superiorly through the ruptured diaphragm (red arrow).
Implementing the Stop the Bleed Campaign in a University Community
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J84D0ZThe main objective is to implement a system to use available resources of the Stop the Bleed campaign to widely educate members of the university community in the utilization of multiple compression techniques including direct pressure, tourniquet application, and wound packing. Additional course objectives include using the Stop the Bleedsm campaign to teach participants how to fit into the emergency response team as the immediate responder and the identification of life-threatening bleeding.
Bilateral Shoulder Dislocation after Ski Injury
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86929An anteroposterior chest X-ray demonstrates bilateral shoulder dislocations. Both the right and left humeral heads (blue lines) are displaced medially, anteriorly, and inferiorly from their normal positions in the glenoid fossae (red lines), thus signifying bilateral anterior dislocations. There is also a fracture of the left humeral head at the greater tubercle (green arrow).
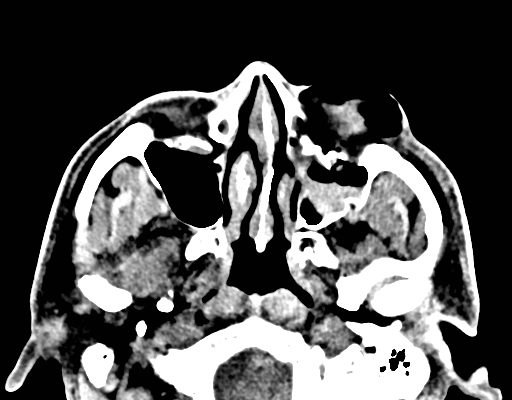
Facial Fracture Induced Periorbital Emphysema
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8F05HPhysical exam showed marked left palpebral subcutaneous crepitus, as well as bulbar and palpebral conjunctival bulging. Visual acuity was normal with intact extraocular movements, and normal pupillary exam. Computed tomography (CT) imaging of the face was obtained and revealed multiple displaced fractures involving the left orbital floor and zygomatic arch associated with moderate periorbital and postseptal extraconal gas, resulting in orbital proptosis.