Respiratory
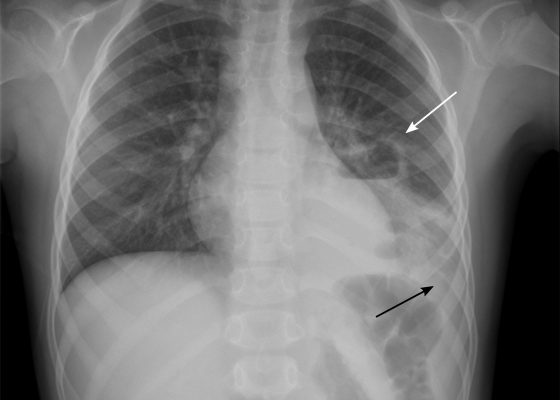
Pediatric Pulmonary Abscess
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83S6QUpright posterior-anterior plain chest films show a left lower lobe consolidation with an air-fluid level and a single septation consistent with a pulmonary abscess (white arrows). A small left pleural effusion was also present, seen as blunting of the left costophrenic angle and obscuration of the left hemidiaphragm (black arrows).
Pneumomediastinum After Cervical Stab Wound
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87P79Anteroposterior (AP) chest X-ray showed subcutaneous emphysema of the neck, surrounding the trachea (red arrows), right side greater than left, and a streak of gas adjacent to the aortic arch (white arrow). Computed tomography angiogram (CTA) of the neck showed air outside of the trachea, positive for pneumomediastinum (blue arrows).
Tricuspid Annular Plane Systolic Excursion (TAPSE) in a Patient with Pulmonary Emboli
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8M052Video 1 and Image 1 show a thrombus in the patient’s IVC. Video 2 and Images 2-3 demonstrate a positive TAPSE of less than 17mm (blue arrow length) with a significantly dilated RV, indicating abnormal excursion of the tricuspid annulus and right ventricular dysfunction.
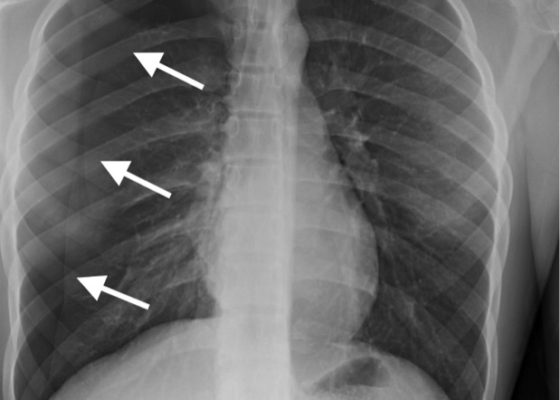
Empyema
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86P9RThe chest X-ray shows a large fluid collection in the right lung demonstrated by the opacification that blunts the costophrenic angle on the right side. There is also a meniscus present, which is generally indicative of fluid. Chest computed tomography (CT) demonstrated an infiltrate with a mixture of densities within the same collection, consistent with a loculated effusion and concerning for an empyema.
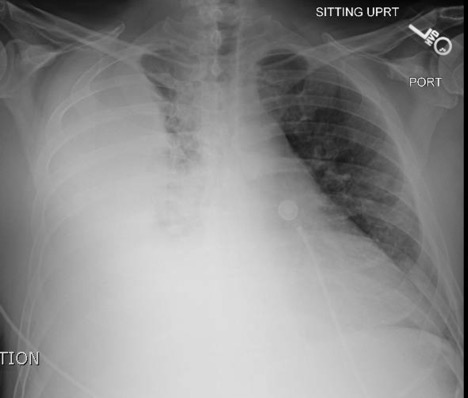
Spontaneous Pneumothorax
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8M33BInitial chest radiograph showed a 50% right-sided pneumothorax with no mediastinal shift, which can be identified by the sharp line representing the pleural lung edge (see arrows) and lack of peripheral lung markings extending to the chest wall. While difficult to accurately estimate volume from a two-dimensional image, a 2 cm pneumothorax seen on chest radiograph correlates to approximately 50% volume.1 The patient underwent insertion of a pigtail pleural drain on the right and repeat chest radiograph showed resolution of previously seen pneumothorax. Ultimately the pigtail drain was removed and chest radiograph showed clear lung fields without evidence of residual pneumothorax or pleural effusion.
Realistic Chest Tube Simulator Using Pork Belly with Skin
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8R03JBy the end of this instructional session learners will be able to: 1) discuss the indications, contraindications, and complications associated with chest tube thoracostomy, 2) competently perform chest tube insertion on a simulator, and 3) properly secure chest tube.
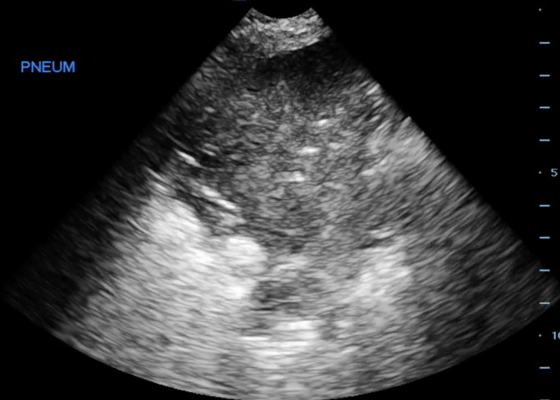
Pneumonia Diagnosed by Point-of-Care Ultrasound
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8XP64Point-of-care ultrasound of the left lower lobe demonstrates lung hepatization, a classic finding for pneumonia. In addition, a shred sign is present with both air bronchograms and focal B-lines—all suggestive of poorly aerated, consolidated lung. The patient was started on antibiotics and admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia.
Re-expansion Pulmonary Edema
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8WS6VInitial chest X-ray (chest X-ray 1) showed a right-sided pleural effusion with compressive atelectasis of the mid to lower right lung. Repeat chest X-ray immediately after evacuation (chest X-ray 2) shows improvement of the pleural effusion and a new trace apical right pneumothorax measuring 6.7 mm. When the patient became tachypneic, a third X-ray (chest X-ray 3) showed persistent trace apical right pneumothorax measuring 6.7 mm.