Cardiology/Vascular
Enhancing Emergency Medicine Resident Education: A Weekly Education Series to Augment Electrocardiogram Education
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8.52141The goals of the curriculum were to establish an asynchronous ECG curriculum to help improve standardization of EM resident education, expose EM residents to a more comprehensive ECG curriculum, increase active learning in this arena, and decrease the administrative burden while not dedicating further conference time towards ECG education.
A Case Report of a 36-year-old Male Diagnosed with a Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection
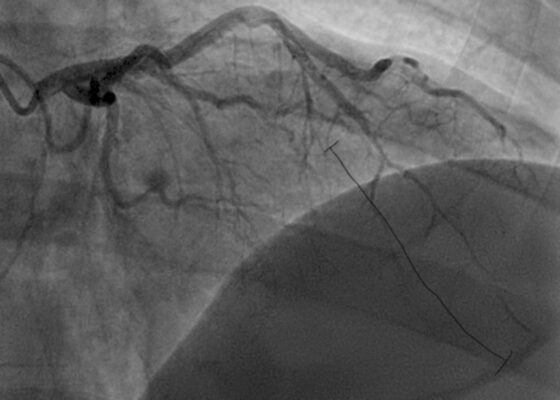
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5070/M5.52022The initial ECG obtained from the patient shows subtle ST-segment elevation noted in leads I, aVL, and V2-V5, suggestive of pathology of the left anterior descending artery. The results of the catheterization revealed a spontaneous coronary artery dissection of the distal portion of the left anterior descending coronary artery, which can be seen in the image of the angiogram, with the diseased portion notated between the brackets.
Effects of Volume Overload: A Case Report of an Edema Bulla
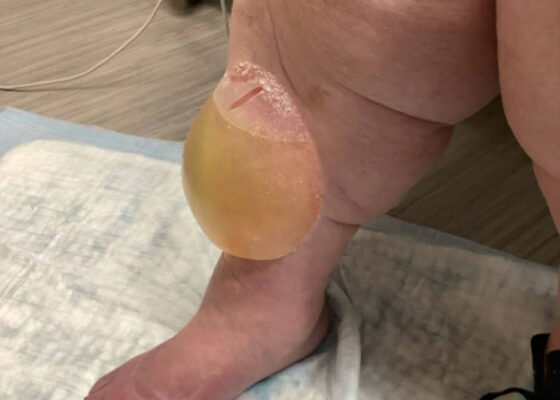
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5070/M5.52206This image shows a large edema bulla on the patient's right shin. The bulla is 10 x 10 cm, filled with serous fluid, has a spontaneously occurring defect in the skin of the superior portion of the bulla, and is non-erythematous. The bulla is much larger than the 1-5 cm edema bullae described in the literature. As edema bulla is primarily a clinical diagnosis, taking the full history and physical exam into account is essential to recognize these bullae.
Ultrasound Case: Syncope in PE
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8.52365By the end of the session, learners will be able to: 1) obtain and interpret the parasternal short-axis view of the heart to assess right ventricular size and function, 2) identify ultrasound findings suggestive of pulmonary embolism (PE) on cardiac short-axis view, including right ventricular dilation and septal bowing, 3) demonstrate appropriate probe selection and positioning to obtain optimal images of the heart and inferior vena cava (IVC), 4) evaluate the IVC using a subxiphoid or longitudinal view to assess distension and lack of respiratory collapse as supportive findings for elevated right heart pressures, 5) identify the anatomy of the neck vasculature, differentiate between the internal jugular vein and carotid artery, and select the appropriate puncture site, 6) describe ultrasound-guided central venous catheterization via the right internal jugular vein, using a sterile technique and real-time guidance