A Case Report of May-Thurner Syndrome Identified on Abdominal Ultrasound
ABSTRACT:
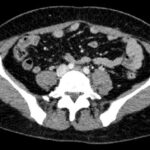
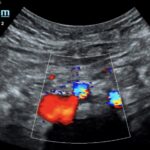
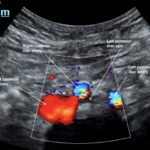
May-Thurner syndrome (MTS) is most commonly caused by the compression of the left iliac vein by the right iliac artery against the lumbar spine, which leads to the development of a partial or occlusive deep venous thrombosis (DVT).1 Diagnosis begins with a duplex ultrasound of the lower extremities to evaluate for a femoropopliteal thrombus, and in high-risk patients where a more proximal DVT is suspected and the DVT ultrasound is negative, a computed tomography venogram (CTV) or magnetic resonance venogram (MRV) is performed.1,3 In this case report, a patient presented to the emergency department (ED) with two days of left lower extremity pain and swelling. Initial lower extremity DVT ultrasound was negative, so a CTV was ordered and revealed a thrombus in the left common iliac vein with overlying compression by the right common iliac artery, suggesting the diagnosis of May-Thurner syndrome (Figure 1). Afterwards, a point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) was performed at bedside to evaluate the caval and iliac arteries and the findings were consistent with the CTV (Figure 2, 3, 4). If the POCUS was performed prior to the CTV, the patient may have been spared the radiation exposure from CT, as well as the risks of intravenous (IV) contrast required for a venogram. Therefore, in high risk patients in whom a negative DVT ultrasound will prompt advanced imaging with CTV or MRV, I propose the addition of a lower abdominal ultrasound using a curvilinear probe to assess the caval and iliac arteries prior to obtaining a CTV or MRV.
Topics:
May-Thurner Syndrome, leg swelling, POCUS, ultrasound, deep venous thrombosis.