Retropharyngeal Abscess in an Adult Patient Presenting with Neck Fullness and Dysphagia: A Case Report
ABSTRACT:
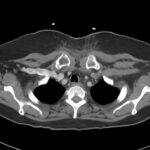
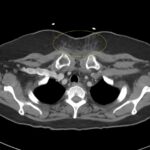
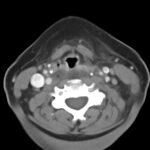
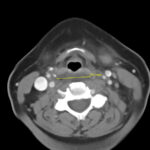
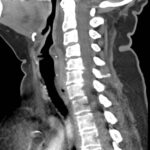
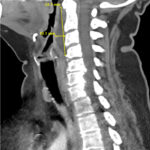
Retropharyngeal abscess (RPA) is an uncommon yet potentially life-threatening condition that is more often seen in young children and may be misdiagnosed in adults presenting with atypical features.1 Retropharyngeal abscess results from spread of antecedent upper respiratory tract infection or traumatic inoculation via foreign body ingestion or medical instrumentation. Clinically, RPA may present with fever, pharyngitis, neck pain, and dysphagia. Diagnosis is often confirmed with imaging studies. We present a case of a 66-year-old female with asthma, hypertension, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) who presented to the emergency department (ED) for evaluation of neck fullness, shoulder pain, dysphagia, and abdominal pain starting less than 24 hours prior to presentation. Computed tomography (CT) revealed a prevertebral/retropharyngeal fluid collection from the odontoid tip to the C4 vertebral body measuring 5.4 x 1.0 x 3.3 centimeters (cm) in size with associated edema at the left neck base extending into the upper chest, suggestive of retropharyngeal abscess. The patient received intravenous (IV) vancomycin and piperacillin/tazobactam and was transferred to a higher level of care for otolaryngologist evaluation. The patient remained stable without airway compromise while in our department. This case underscores challenges in diagnosing atypical presentations of RPA in adults, emphasizing timely recognition to prevent complications.
Topics:
Dysphagia, retropharyngeal abscess, prevertebral abscess, otolaryngology.