Cholelithiasis: WES Sign
History of present illness:
A 33-year-old female with multiple previous episodes of biliary colic presented to the emergency department with severe right upper quadrant pain that started 30 minutes prior to arrival. She characterized her pain as sharp and pulling and radiating to the back. Upon physical examination, patient was in acute distress with severe tenderness to right upper quadrant palpation. Her abdomen was soft, with no guarding or rebound tenderness.
Significant findings:
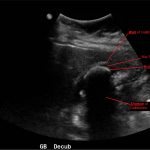
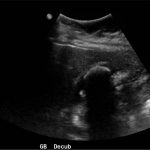
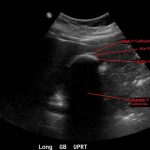
Abdominal ultrasound showed the classic presentation of the Wall-Echo-Shadow (WES) sign. The superficial aspect of the gallbladder wall is represented by a hyperechogenic curve. Below this, bile fluid is represented by hypoechogenicity. Underneath the bile fluid is the echo of the dense border created by the collection of gallstones, represented by a hyperechogenic curve. Due to the high density of the gallstones, nothing deeper can be visualized (including other gallstones or the far end of the gallbladder); this is the shadow.
Discussion:
The WES sign, first described in the early 1980s, is a clear way of identifying cholelithiasis when the condition has progressed to fill the entire lumen of the gallbladder.1 In this case, the lumen of the gallbladder looks hypoechogenic relative to the surrounding tissue, much like an empty gallbladder. This is due to the border of the dense stones opposing the near wall of the gallbladder casting a shadow over everything distal to the stones. These key visualization techniques decrease non-visualization of chronic cholelithiasis.2,3,4 In most cases, WES sign is sufficient to diagnose cholelithiasis. Of note, “porcelain gallbladder” or collapsed duodenum can have the potential produce similar ultrasonographic findings.4,5
Topics:
Ultrasound, gallbladder, WES, wall echo shadow, cholelithiasis, gallstones, abdominal pain.
References:
- Macdonald FR, Cooperberg PL, Cohen MM. The WES triad – a specific sonographic sign of gallstones in the contracted gallbladder. Gastrointest Radiol. 1981;6(1):39-41. doi: 10.1007/BF01890219
- George N, Dawkins A, Disantis D. The wall-echo-shadow (WES) sign. Abdom Imaging. 2015;40(7):2903. doi: 10.1007/s00261-015-0401-4
- Raptopoulos V, D’orsi C, Smith E, Reuter K, Moss L, Kleinman P. Dynamic cholecystosonography of the contracted gallbladder: the double-arc-shadow sign. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1982;138(2):275-278. doi: 10.2214/ajr.138.2.275
- Rybicki FJ. The WES sign. Radiology. 2000;214(3):881-882. doi: 10.1148/radiology.214.3.r00mr38881
- Solomon DM, Paippattuthara J, Zoberman H, Hahn B. Images in emergency medicine: wall-echo-shadow (WES) complex. J Emerg Med. 2012;43(3):e203-204. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2011.01.001