Visual EM
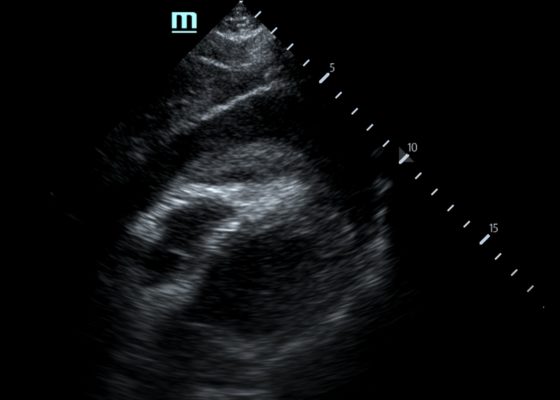
Pericardial Clot on Point-of-Care Ultrasound
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8ZH1TFocused assessment with sonography in trauma (FAST) scan was positive for a clinically significant pericardial effusion as evidenced by the hypoechoic fluid around the myocardium, indicated by the blue arrow in image 2. Findings are also consistent with tamponade process as evidenced by restricted expansion and collapse of the right ventricle during diastole. The hyperechoic floating structure between the pericardium and myocardium, adjacent to the right ventricle, represents a pericardial clot, indicated by the white arrow.The density of the pericardial clot differs from that of the myocardium, thus serving as an additional variable to avoid confusing this as part of the myocardial structure.
Wellens’ Syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8FS8KInitial electrocardiogram (ECG) revealed the classic biphasic T waves in V2 and V3 of Wellen’s syndrome (see red outlines). A second EKG demonstrated an evolving deeply inverted T wave (see blue outlines).
Arteriovenous Graft Pseudoaneurysm
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8B06ZA bedside ultrasound of the mass demonstrated a large compressible hypoechoic structure (see purple outline) above the arteriovenous graft (see red outline). The contents demonstrated movement of fluid within the structure. This was confirmed with Doppler mode, which allowed for visualization of flow communicating between the structure and the underlying vessel, which is diagnostic for a pseudoaneurysm.
Bilateral Shoulder Dislocation after Ski Injury
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86929An anteroposterior chest X-ray demonstrates bilateral shoulder dislocations. Both the right and left humeral heads (blue lines) are displaced medially, anteriorly, and inferiorly from their normal positions in the glenoid fossae (red lines), thus signifying bilateral anterior dislocations. There is also a fracture of the left humeral head at the greater tubercle (green arrow).
Abdominal Pain with Black Tongue
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8XS7JPatient’s tongue had a black discoloration, without elongated filiform papillae. We could not appreciate lymphadenopathy. His abdomen was tender to palpation.
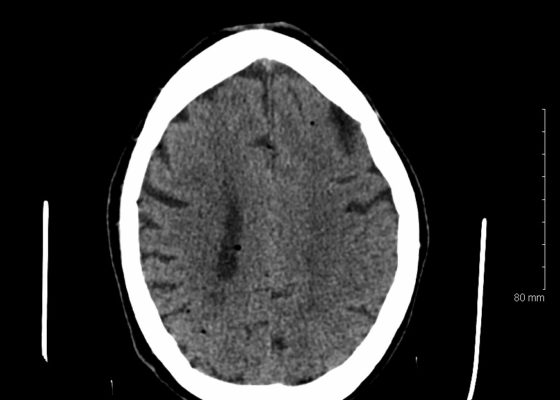
Beware the Devastating Outcome of a Common Procedure
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8T336Non-contrast head computed tomography (CT) demonstrates multifocal bilateral hypodense lesions (white arrows) representing air emboli. Note the lesions are located in the intra-axial distribution which indicates an underlying vascular origin.
Suspicious Skin Lesion in an 11-Year-Old Male
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8JK9TThe patient had a 5 cm ulcerative lesion with raised borders and a yellow, “fatty” center. There was no active drainage, site tenderness, or lymphadenopathy.
Guilty as Charged: Jailed Coronary Vessel Presenting as Wellens’ Syndrome Type B
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8DS6HEvolving changes to electrocardiograph (ECG) were noted during serial ECG monitoring involving leads V2 and V3, along with some T-wave inversion in V4 and V5 that were concerning for a Wellens’ syndrome type B on second ECG. She was admitted and subsequently taken to cardiac catheterization suite where it was revealed that the previously placed stent in the left anterior descending (LAD) artery was patent. Unfortunately, the stent blocked off an adjacent side branch vessel off the LAD in proximal two-third region of the stent (as seen in the cartoon).