Posts by JETem
Febrile Seizure Simulation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J81018At the end of this simulation session, the learner will be able to: 1) discuss the management of febrile seizures 2) discuss when placement of an advanced airway is indicated in the management of a febrile seizure 3) list the risk factors for febrile seizures 4) prepare a differential diagnosis for the causes of febrile seizures 5) educate family members on febrile seizures.
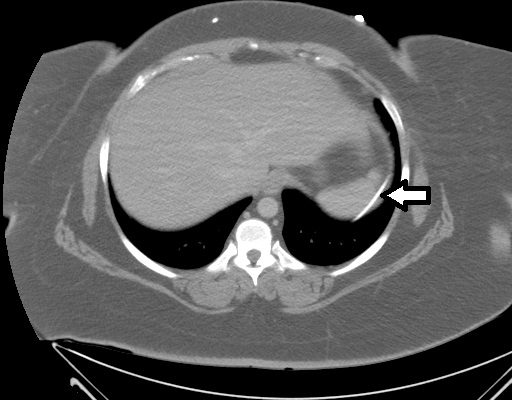
An Elderly Female with Dyspnea and Abdominal Pain
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83S3KRadiography shows a dilated, gas-filled structure that fills nearly the entire left hemi-thorax. Lung markings are visible in the uppermost portion of the left hemi-thorax. There is mediastinal shift to the right. In the visualized portion of the abdomen, dilated loops of bowel are also visualized. This constellation of findings is consistent with a tension gastrothorax.
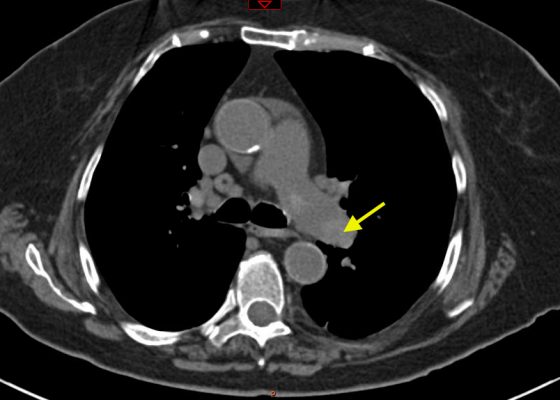
Pulmonary Embolism: Diagnosis by Computerized Tomography without Intravenous Contrast
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8001ZNon-contrast CT of the chest demonstrates hyper-densities within both central and sub-segmental pulmonary arteries bilaterally (see yellow arrows). The right ventricle is dilated.
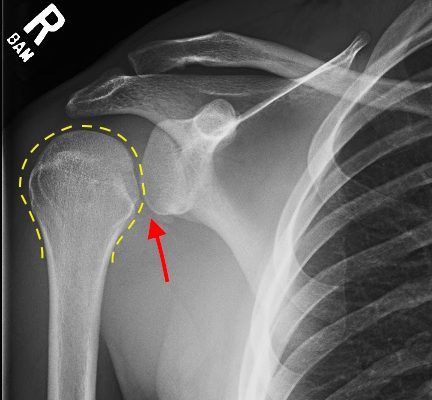
Irreducible Traumatic Posterior Shoulder Dislocation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8V884Radiographs demonstrated posterior displacement of the humeral head on the “Y” view (see white arrow) and widening of the glenohumeral joint space on anterior-posterior view (see red arrow). The findings were consistent with posterior dislocation and a Hill-Sachs type deformity. Sedation was performed and reduction was attempted using external rotation, traction counter-traction. An immediate “pop” was felt during the procedure. Post-procedure radiographs revealed a persistent posterior subluxation with interlocking at posterior glenoid. CT revealed posterior dislocation with acute depressed impaction deformity medial to the biceps groove with the humeral head perched on the posterior glenoid, interlocked at reverse Hill-Sachs deformity (see blue arrow).
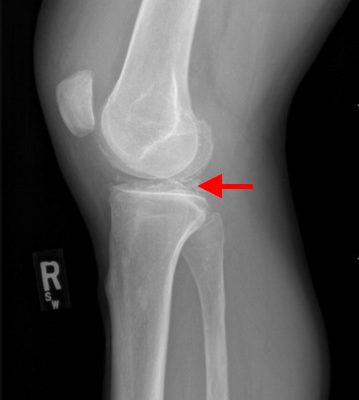
Pseudogout and Calcium Pyrophosphate Disease
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QG66Radiographs of the knee showed multiple radio-dense lines paralleling the articular surface (see red arrows) consistent with calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition within the joint often seen in calcium pyrophosphate disease (CPPD) also known as pseudogout.
ST Elevation in aVR with Coexistent Multilead ST Depression
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KS3XThe ECG shows ST-segment depressions in precordial leads V3 through V6, and limb leads I, II, and aVL, and 1 mm of ST-segment elevation in aVR. The initial troponin I was elevated at 1.37 ng/mL (upper limit of normal 0.40). Cardiology decided to delay catheterization until the next day when diffuse coronary disease was discovered (including 90% of the left circumflex stenosis, 60% proximal and 75% mid-left anterior descending stenosis, 75% third diagonal branch stenosis, and 90% posterior descending artery stenosis). The following day, the patient went to the operating room for coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Migration
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8G019An immediate post-op abdominal x-ray performed after the patient’s VP shunt revision 30 days prior to this ED visit reveals the VP shunt tip in the mid abdomen. A CT of the abdomen performed on the day of the ED visit reveals the VP shunt tip interposed between the spleen and the diaphragm.
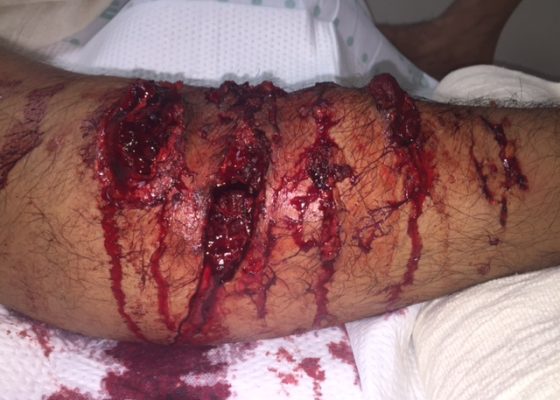
K-9 Police Dog Bite
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8B88GThe photograph is of the anterior compartment of the right lower leg demonstrating multiple deep lacerations with exposed and torn muscle. X-ray showed no foreign body.