Posts by JETem
Infectious Mononucleosis: Pharyngitis and Morbilliform Rash
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88C7HHer physical exam was significant for bilateral tonsillar exudates, cervical lymphadenopathy, and a morbilliform rash that included the palms (Figure 1-4). Laboratory testing was significant for white blood cell (WBC) count of 16.5 thous/mcl with an elevation in absolute lymphocytes of > 10 thous/mcl. The monospot and EBV (Epstein-Barr virus) panel were positive.
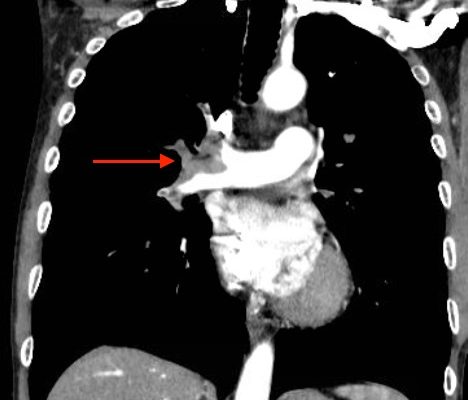
Acute, massive pulmonary embolism with right heart strain and hypoxia requiring emergent tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) infusion
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J84K5KCT angiogram showed multiple large acute pulmonary emboli, most significantly in the distal right main pulmonary artery (image 1 and 2). Additional pulmonary emboli were noted in the bilateral lobar, segmental, and subsegmental levels of all lobes. There was a peripheral, wedge-shaped consolidation surrounded by groundglass changes in the posterolateral basal right lower lobe that was consistent with a small lung infarction (image 3).
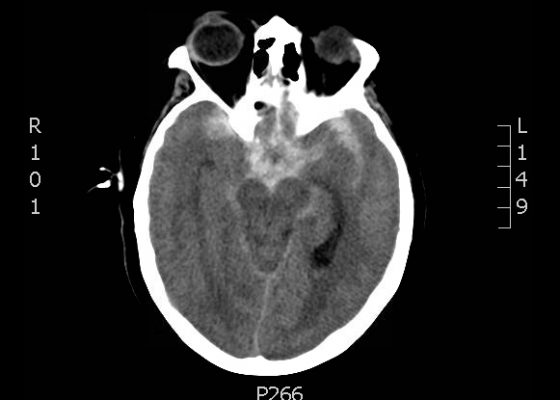
Presentation of Significant Subarachnoid Hemorrhage without Loss of Consciousness
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J80W29A non-contrast head CT demonstrated extensive subarachnoid hemorrhage occupying both cerebral convexities, the anterior interhemispheric fissure, the sylvian fissures, and the basal cisterns. Later CTA would show an 8 mm by 7 mm by 8mm MCA aneurysm near the M1/M2 junction and two pericallosal artery aneurysms, 7 by 6 mm and 8 by 5 mm respectively.
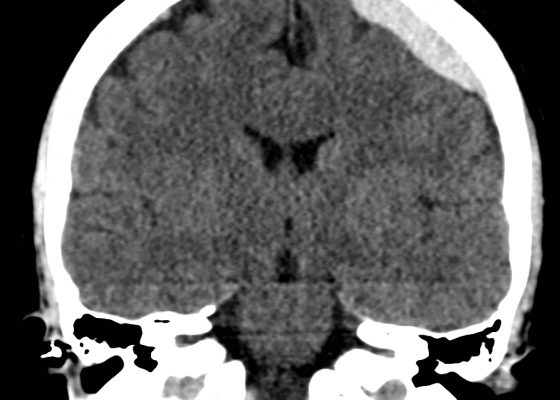
Acute Subdural Hematoma
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87C76Non-contrast Computed Tomography (CT) of the Head showed a dense extra-axial collection along the left frontal and parietal regions, extending superior to the vertex with mild mass effect, but no midline shift.
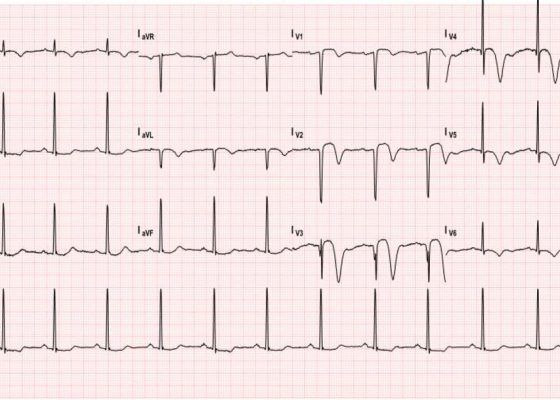
Wellens’ Sign (Wellens’ Syndrome)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8W30PThis EKG shows deep, inverted T waves that are most pronounced in V2-V4, and are associated with continued T wave inversions in V5 and V6 and ST segment changes in V1-V3.
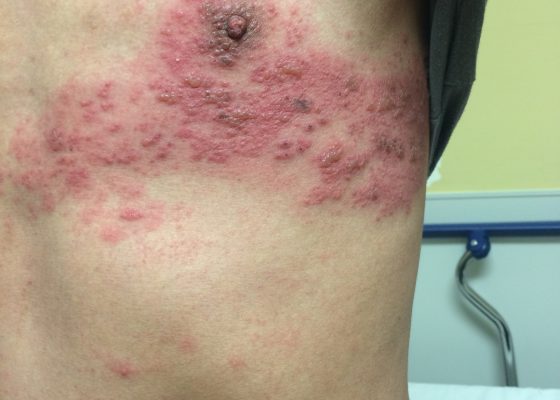
Herpes Zoster
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8C301The patient was in mild distress, afebrile, with stable vital signs. His physical exam revealed an erythematous, grouped vesicular rash in various stages of progression including erythematous papules, clear vesicles, and pustular vesicles. Few lesions were scabbed over. No signs of crusting or scarring were appreciated. The distribution encompassed the entire left T4 dermatome both posteriorly and anteriorly. No other rashes were appreciated elsewhere on the body.
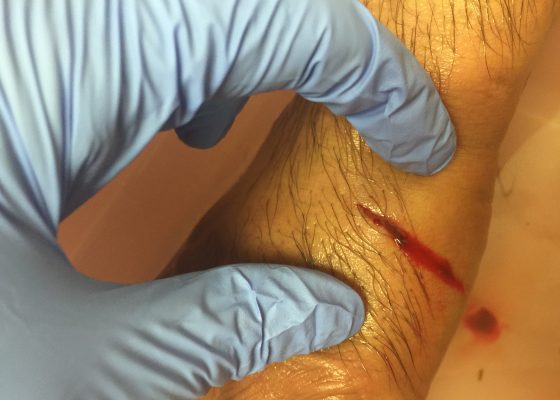
Stingray Envenomation
DOI: http://doi.org/10.21980/J86C7WPhysical exam revealed a 3cm laceration to the ulnar side of the dorsum of the left hand with minimal hand swelling. There was no exposed tendon or bone, the hand was neurovascularly intact and had full strength. A small barb was visualized and removed from the injury site. Radiograph of the left hand confirmed that there was no remaining barb (see normal x-ray).
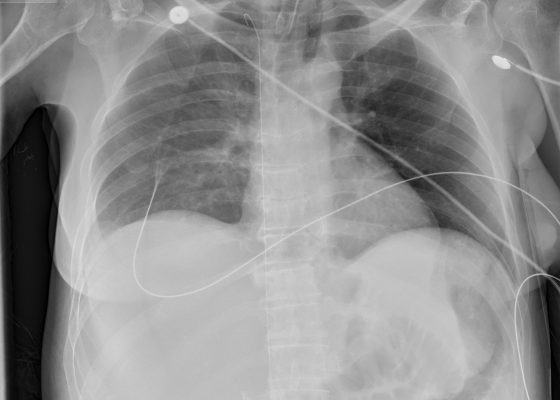
The Lost Guidewire
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82P4MInitial chest radiograph shows a guidewire in the inferior vena cava (IVC), superior vena cava (SVC), and right IJ veins.