Issue 2:2
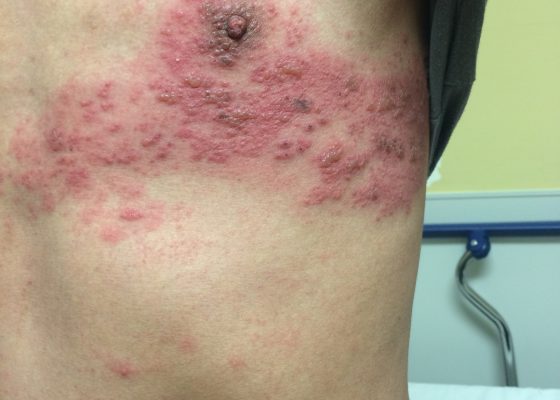
Herpes Zoster
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8C301The patient was in mild distress, afebrile, with stable vital signs. His physical exam revealed an erythematous, grouped vesicular rash in various stages of progression including erythematous papules, clear vesicles, and pustular vesicles. Few lesions were scabbed over. No signs of crusting or scarring were appreciated. The distribution encompassed the entire left T4 dermatome both posteriorly and anteriorly. No other rashes were appreciated elsewhere on the body.
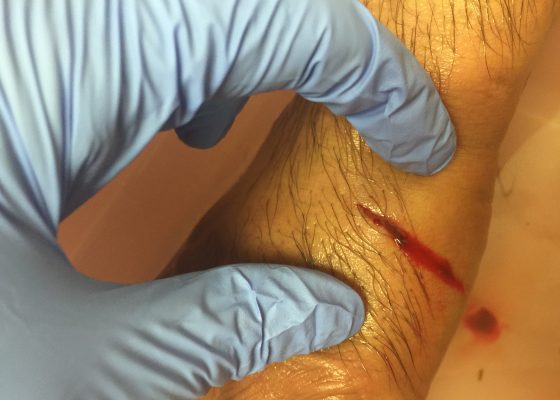
Stingray Envenomation
DOI: http://doi.org/10.21980/J86C7WPhysical exam revealed a 3cm laceration to the ulnar side of the dorsum of the left hand with minimal hand swelling. There was no exposed tendon or bone, the hand was neurovascularly intact and had full strength. A small barb was visualized and removed from the injury site. Radiograph of the left hand confirmed that there was no remaining barb (see normal x-ray).
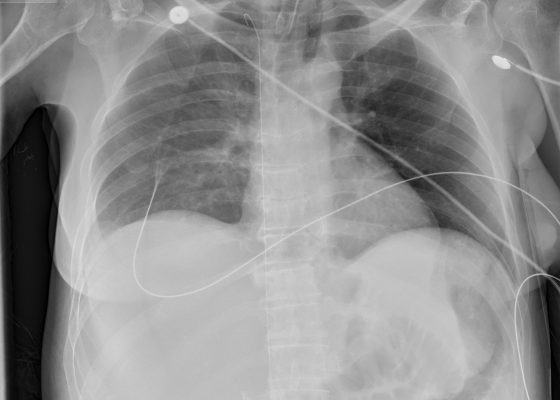
The Lost Guidewire
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82P4MInitial chest radiograph shows a guidewire in the inferior vena cava (IVC), superior vena cava (SVC), and right IJ veins.
A Toddler with Abdominal Pain and Emesis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8XW2PIn the long axis video, the appendix appears as an enlarged, non-compressible, blind-ending tubular structure (white arrow) with distinct appendiceal wall layers and lack of peristalsis. In the short axis video, the appendix appears as a target sign (yellow arrow) between the abdominal and psoas muscles. The maximal outer diameter (MOD) measures 11.8mm and the appendix wall measures 0.17mm. There is trace adjacent free fluid and echogenic periappendiceal fat. Transverse axis video and image (red arrow) demonstrate that the appendix is not compressible. These findings are consistent with acute appendicitis.