Posts by JETem
Acetabular Fracture
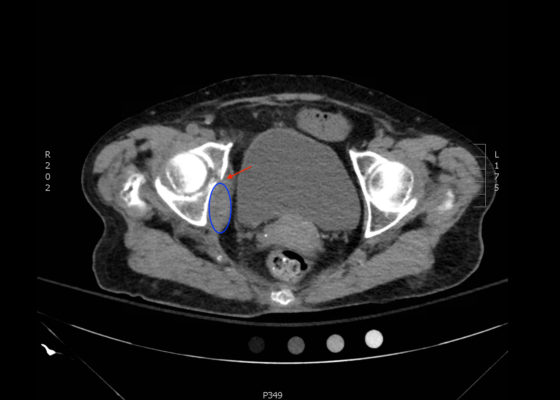
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BK8KThe non-contrast CT images show a minimally displaced comminuted fracture of the right acetabulum involving the acetabular roof, medial and anterior walls (red arrows), with associated obturator muscle hematoma (blue oval).
Bedside Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Obstruction
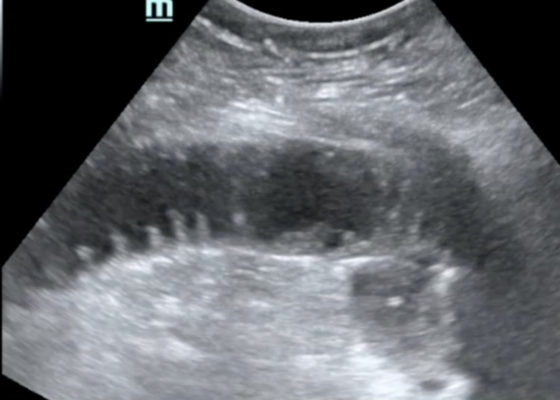
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86W6PThe POCUS utilizing the low frequency curvilinear probe demonstrates fluid-filled, dilated bowel loops greater than 2.5cm with to-and-fro peristalsis, and thickened bowel walls greater than 3mm, concerning for SBO.
Chancre of Primary Syphilis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83342Physical examination revealed a non-tender, erythematous lesion on the glans penis, two similar adjacent satellite lesions, as well as tender inguinal lymphadenopathy. No penile discharge was noted.
Novel Emergency Medicine Curriculum Utilizing Self-Directed Learning and the Flipped Classroom Method: Psychiatric Emergencies Small Group Module
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8DP7VWe aim to teach the presentation and management of psychiatric emergencies through the creation of a flipped classroom design. This unique, innovative curriculum utilizes resources chosen by education faculty and resident learners, study questions, real-life experiences, and small group discussions in place of traditional lectures. In doing so, a goal of the curriculum is to encourage self-directed learning, improve understanding and knowledge retention, and improve the educational experience of our residents.
Novel Emergency Medicine Curriculum Utilizing Self-Directed Learning and the Flipped Classroom Method: Genitourinary Emergencies Small Group Module
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J89S56We aim to teach the presentation and management of genitourinary emergencies through the creation of a flipped classroom design. This unique, innovative curriculum utilizes resources chosen by education faculty and resident learners, study questions, real-life experiences, and small group discussions in place of traditional lectures. In doing so, a goal of the curriculum is to encourage self-directed learning, improve understanding and knowledge retention, and improve the educational experience of our residents.
Emergency Medicine Curriculum: Complications of Pregnancy Small Group Module
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TS67We aim to teach the presentation and management of pregnancy complications through interactive teaching during small group discussions concerning patient cases. This curriculum utilizes resources chosen by education faculty, study questions, actual experience, and small group discussions in place of a traditional lecture-based format. In doing so, a goal of the curriculum is to encourage self-directed learning, improve understanding and knowledge retention, improve the educational experience of our residents, and allow assessment by the faculty concerning the knowledge base and ability of the residents.
A Simulation Model for Extensor Tendon Repair
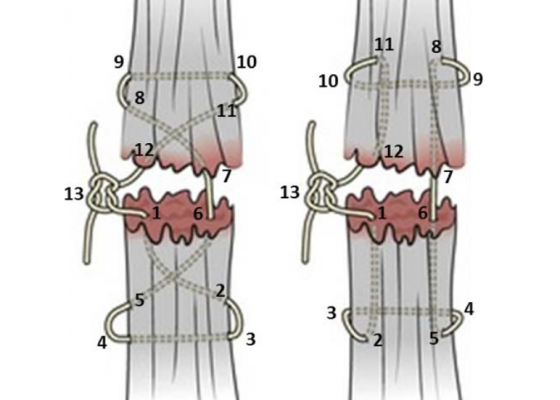
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VS7XBy the end of this educational session, the learner will be able to: 1) List the indications for extensor tendon repair in the emergency department, 2) recognize the indications for referral to orthopedic or hand surgery, 3) list the risks and benefits of emergency department extensor tendon repair, 4) perform an appropriate physical examination for a patient with a potential extensor tendon laceration, 5) list the maximum time limit of tourniquet application for this procedure, 6) list the materials needed for extensor tendon repair in the emergency department, 7) successfully repair a completely severed extensor tendon using four different techniques: horizontal mattress, figure of eight, modified Kessler and modified Bunnell, and 8) describe the appropriate splinting of a repaired extensor tendon.
Realistic Chest Tube Simulator Using Pork Belly with Skin
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8R03JBy the end of this instructional session learners will be able to: 1) discuss the indications, contraindications, and complications associated with chest tube thoracostomy, 2) competently perform chest tube insertion on a simulator, and 3) properly secure chest tube.