Posts by JETem
Novel Emergency Medicine Curriculum Utilizing Self-Directed Learning and the Flipped Classroom Method: Endocrine and Metabolic Emergencies Small Group Module
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8792MWe aim to teach the presentation and management of endocrine emergencies through the creation of a flipped classroom design. This unique, innovative curriculum utilizes resources chosen by education faculty and resident learners, study questions, real-life experiences, and small group discussions in place of traditional lectures. In doing so, a goal of the curriculum is to encourage self-directed learning, improve understanding and knowledge retention, and improve the educational experience of our residents.
Low-Cost, Low Fidelity Meat Model to Teach Ultrasound Guided Nerve Blocks
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83G9RUpon completion of this workshop, learners will be able to: 1) Describe the risks and benefits of ultrasound guided nerve blocks. 2) Choose the appropriate nerve to block based on the area that needs anesthesia. 3) Display proficiency in performing an ultrasound guided nerve block on meat models. 4) Verbalize confidence in successfully performing ultrasound guided regional anesthesia. By successfully meeting these objectives, we aim to improve learner confidence and clinical ability in performing ultrasound guided nerve blocks.
Pediatric Airway Team Based Learning
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KH01This cTBL covers a variety of pediatric airway emergencies. Therefore, by the end of this cTBL, the learner will be able to: 1) List the signs and symptoms associated with airway foreign body obstructions. 2) State the appropriate management of upper and lower airway foreign bodies. 3) Discuss the symptoms, signs, and management of bacterial tracheitis. 4) Discuss a step-wise algorithm for emergency asthma treatment in the emergency department setting. 5) Identify the potential complications of tonsillectomy and the acute management of post-tonsillectomy hemorrhage.
Cocaine-induced Myocardial Infarction and Pulmonary Edema
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8ZS87By the end of this simulation session, the learners will be able to:1) Determine appropriate diagnostics in a patient with likely cocaine toxicity. 2) Identify and manage respiratory failure. 3) Identify and manage a ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and pulmonary edema. 4) Identify and manage cocaine toxicity with benzodiazepines. 5) Determine appropriate disposition of the patient to the cardiac catheterization lab and an intensive care unit (ICU). 6) Demonstrate effective communication and teamwork during resuscitation of a critically ill patient.
Prehospital Cardiac Arrest Management Simulation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8V057At the end of this simulation learners will be able to: 1) Perform team-focused CPR using effective leadership and communication skills during prehospital resuscitation. 2) Employ high-quality CPR with an emphasis on compressions and early defibrillation. 3) Demonstrate appropriate airway management utilizing an oropharyngeal airway and bag-valve-mask, blind-insertion airway device, and/or endotracheal intubation during cardiac arrest. 4) Recognize and appropriately defibrillate pulseless ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. 5) Formulate an appropriate differential diagnosis for pulseless electrical activity.
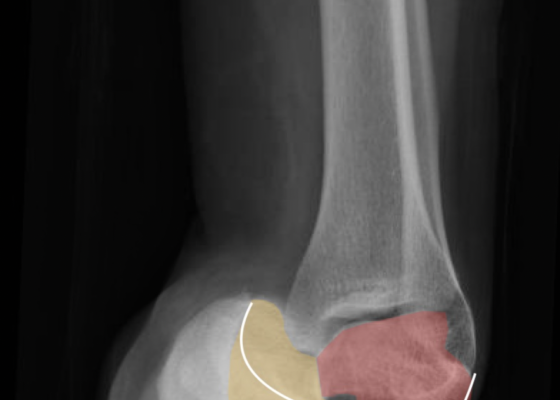
Talonavicular Dislocation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8PG91The X-rays were significant for a subtalar dislocation. The calcaneus (red) is laterally displaced with respect to the talar head (orange), and the white lines indicate the normal articular surface. Additionally, there was a talonavicular dislocation, as seen in the fourth image: the talus (green) and navicular bone (purple) overlapping suggests a dislocation. In a normally aligned foot, the boundaries of the two bones create a point of articulation.
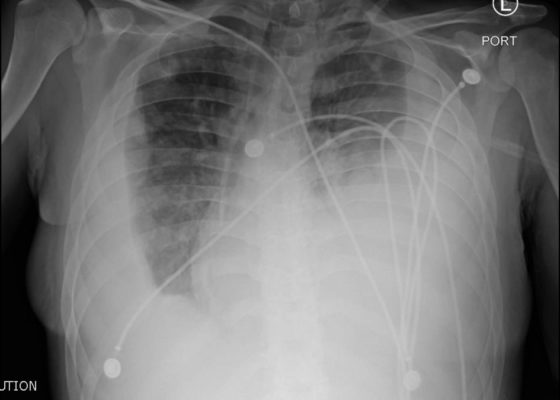
Endocarditis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8JP73Upright frontal radiograph of the chest demonstrated large pleural effusion on the left and moderate pleural effusion on the right as shown by the visible menisci on both sides (red arrows) with diffuse bilateral nodular densities (yellow dotted lines), consistent with septic pulmonary emboli. Computed tomography (CT) of the chest demonstrated multiple scattered lung nodules bilaterally containing internal foci of air cavitation (green dotted lines).