Posts by JETem
Emergency Medicine Curriculum Utilizing the Flipped Classroom Method: Environmental Emergencies
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TP8ZThrough a flipped classroom design, we aim to teach the presentation and management of environmental emergencies, specifically cold related illness, heat related illness, undersea medicine, high altitude medicine, submersion, electrocution, radiation injury, and envenomation. This unique, innovative curriculum utilizes resources chosen by education faculty and resident learners, study questions, real-life experiences, and small group discussions in place of traditional lectures. In doing so, a goal of the curriculum is to encourage self-directed learning, improve understanding and knowledge retention, and improve the educational experience of our residents.
Google Forms – A Novel Solution to Blended Learning
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BP77By the end of the session, the learner should be able to create a didactic session utilizing Google Forms (or similar web-based application). Specific learning objectives for the didactic session will vary based on application. Our institution has used Google Forms to create case-based small group discussion sessions, “create your own adventure” individual learning cases, asynchronous learning opportunities, and interactive intra-lecture surveys.
The Gravid Watermelon: An Inexpensive Perimortem Caesarean Section Model
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8705NThe gravid watermelon is a cost-effective model that uses common materials from the supermarket and emergency department (ED), using a carved-out watermelon as a base, representing the peritoneal cavity. Inexpensive respiratory tubing is used to represent intestine; watered down gelatin and a small doll in a deflated rubber/plastic ball is used to represent a gravid uterus. The bladder is represented by an unused, water-filled exam glove, and watermelon pulp represents blood clots and mesentery. The gravid watermelon is covered with an elastic bandage to represent tough muscle and fascia, and topped with a shower curtain for skin.
Low-Cost Portable Suction-Assisted Laryngoscopy Airway Decontamination (SALAD) Simulator for Dynamic Emesis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8362BThe economic and dynamic SALAD innovation recreates an actively vomiting patient and replicates visual obstruction from fluid contents during airway management.By the end of the session, learners are expected to: 1) discuss the risks, benefits, indications and contraindications associated with intubation of a vomiting or hemorrhaging patient. 2) Work with colleagues to effectively stabilize a patient who is actively vomiting or bleeding during airway management. 3) Competently perform intubation in the acute setting of visual obstruction from active emesis, hemorrhage, or massive regurgitation. 4) Increase speed and dexterity of intubation by applying the SALAD method when fluid obstructs visualization of the larynx.
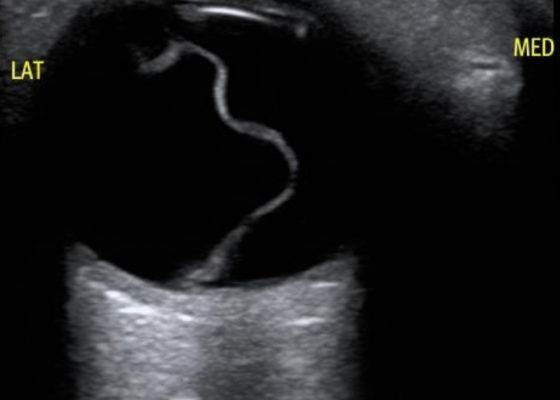
Macula-Off Retinal Detachment Identified on Bedside Ultrasound
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8WP8KPoint-of-care ultrasound was performed, demonstratinga free-floating, serpiginous, hyperechoic membrane (R) tethered at the optic nerve (ON) and ora serrata (OS), but detached at the macula (M) lateral to the optic nerve. This is diagnostic for macula-off retinal detachment. It can be differentiated from macula-on retinal detachment, in which the hyperechoic retina would appear attached posteriorly at the location of the macula just lateral to the optic nerve. Ophthalmology was consulted, agreed with the diagnosis of macula-off retinal detachment, and took the patient to the OR for laser photocoagulation.
Point-of-Care Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Systolic Heart Failure
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8HD1RBedside ultrasound with the phased array probe was used to obtain a parasternal long axis view which demonstrated poor contractility and a severely decreased ejection fraction (EF). M-mode was placed over the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve to create a tracing depicting both the E-wave of early diastole (green arrow) and the A-wave from the atrial kick (blue arrow). The shortest distance between the septum and the mitral valve on the M-mode tracing gives the patient’s E-Point Septal Separation (EPSS) (pink arrow). EF can be estimated using the formula EF=75.5-2.5 x EPSS (in mm). This patient’s EPSS was measured to be 20mm which estimates that she had an EF of 25.5%.
Bedside Ultrasound for the Rapid Diagnosis of Fournier’s Gangrene
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8CP99Point of care ultrasound (POCUS) utilizing a high-frequency linear probe revealed heterogeneous debris with subcutaneous air within the scrotal wall extending into the perineum consistent with necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum or Fournier’s gangrene (FG). The video shows multiple foci of gas that appear as echogenic dots with “dirty shadows” posteriorly from reverberation artifact arising from gas within the soft tissue.
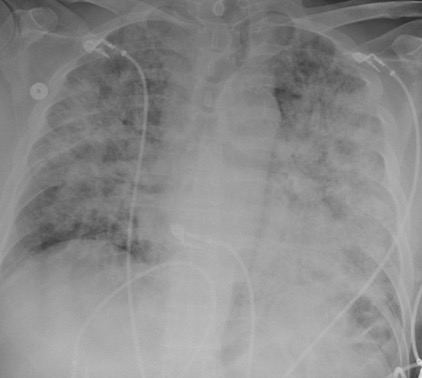
Pneumocystis jirovecii (carinii) Pneumonia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8RW6NChest X-ray showed diffuse, patchy interstitial and alveolar infiltrates bilaterally concerning for Pneumocystis jirovecii(previously Pneumocystis carinii) pneumonia (PJP). The AP radiograph (top left figure) showed the classic “bat-wing” distribution on the left side. Repeat radiograph (bottom figure) one day after admission showed worsening of the infiltrates.