Issue 9:3
Utilization of an Asynchronous Online Learning Module Followed by Simulated Scenario to Train Emergency Medicine Residents in Mass-Casualty Triage
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J89S7ZThe purpose of this session is to train EM residents in the use of the Simple Triage and Rapid Treatment (START) and pediatric JumpSTART algorithms for triage in mass casualty incidents (MCIs) using an asynchronous model. By the end of this small group session, learners will be able to: 1) describe START triage for adult MCI victims; 2) describe JumpSTART triage for pediatric MCI victims; 3) demonstrate the ability to apply the START and JumpSTART triage algorithms in a self-directed learning environment; 4) demonstrate the ability to apply the START and JumpSTART triage algorithms in a simulated mass casualty scenario under time constraints; and 5) demonstrate appropriate use of acute life-saving interventions as dictated by the START and JumpSTART triage algorithms in a high-pressure simulated environment.
Development and Design of a Pediatric Case-Based Virtual Escape Room on Organophosphate Toxicity
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8DH1VBy the end of the activity, learners should be able to: 1) recognize risk factors, symptoms, and presentation for organophosphate poisoning; 2) understand the radiologic and laboratory findings in organophosphate poisoning; 3) distinguish and differentiate electrocardiogram findings in common toxic ingestions; 4) explain the pathophysiology of organophosphate poisoning; 5) understand the importance of decontamination of the patient and personal protective equipment for staff for organophosphate poisoning; 6) describe the airway management of organophosphate poisoning; 7) describe the medical management of organophosphate poisoning, including antidotes and the correct dosing and 8) demonstrate teamwork through communication and collaboration.
First Aid Curriculum for Second Year Medical Students
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8FH2JSmall group activities were performed with a focus on case-based scenarios combined with hands-on instruction. The four scenarios were choking, seizure, anaphylaxis, and bleeding which were taught by an educator who was either faculty, an emergency medicine resident, or an upper-level medical student. Facilitators were provided an educational handout specific to their station to guide them through the teaching session. A PowerPoint presentation was also provided complete with supporting images and videos to share with the students each session.
Identification of a Human Trafficking Victim: A Simulation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8293FBy the end of this simulation, participants will be able to: (1) Identify signs of human trafficking. (2) Demonstrate the ability to perform a primary and secondary assessment of a patient when there is concern for human trafficking. (3) Demonstrate the ability to appropriately separate an at-risk patient from a potential trafficker. (4) Identify resources and a reliable course of action to permanently remove the patient from the harmful situation.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causing a Seizure: An Assessment Simulation for Medical Students
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8XH1HAt the conclusion of the simulation leaners will be able to: 1) efficiently take a history from the patient and perform a physical exam (including a complete neurological exam); 2) identify red flag symptoms in a patient complaining of a headache; 3) order and interpret the results of a CT of the head and either a CT angiogram of the brain or a lumbar puncture to make the diagnosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage; 4) demonstrate appropriate management of a seizure; and 5) utilize the I-PASS framework to communicate with the inpatient team during the transition of care.
High-Fidelity Simulation with Transvaginal Ultrasound in the Emergency Department
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8606QBy the end of the session, learners should be able to 1) recognize the clinical indications for transvaginal ultrasound in the ED, 2) practice the insertion, orientation, and sweeping motions used to perform a TVPOCUS study, 3) interpret transvaginal ultrasound images showing an IUP or alternative pathologies, and 4) understand proper barrier, disinfection, and storage techniques for endocavitary probes.
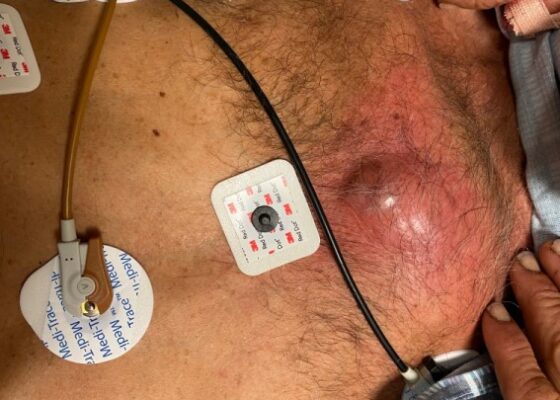
A Man With Chest Pain After An Assault – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8J93SOn exam, we found a suspected chest wall abscess with surrounding erythema (blue arrow). The patient underwent CT of the chest which showed a comminuted displaced midsternal fracture (yellow arrow) with moderate fluid and air anteriorly (red arrow), consistent with an abscess. His laboratory results had no significant abnormalities.
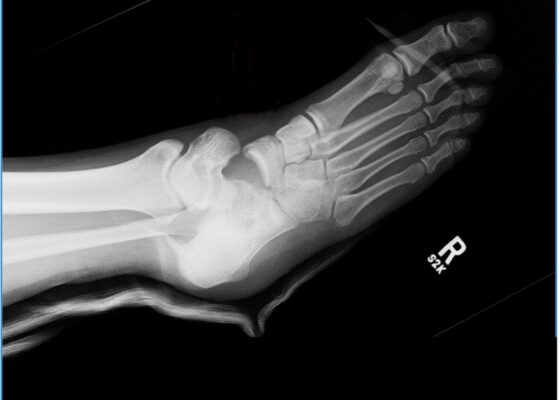
A Case Report of Lateral Subtalar Dislocation: Emergency Medicine Assessment, Management and Disposition
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8SS8PIn a lateral subtalar dislocation, the navicular bone (red bone in 3D anatomy image) and the calcaneus (yellow bone in 3D anatomy image) dislocate laterally in relation to the talus (lavender bone in 3D anatomy image). Plain film oblique and lateral X-rays demonstrate the initial dislocation (talus in red, navicular in blue). It is clear in the initial lateral view that there is loss of the talar/navicular articulation (noted by red arrow). The anterior-posterior x-ray is more challenging to discern the anatomy; however, the talus (red dot) is laterally displaced in comparison to the navicular (blue dot).
1›
Page 1 of 2