Issue 4:4
Classic Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BD16The pelvis X-ray demonstrates a widened right capital femoral epiphysis (more than 2 mm) that is typical of a slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE).1 The yellow highlight outlines this area of widening.
The classic Klein’s line (orange lines) is often inaccurate and even difficult to draw with certainty.1 Nevertheless, in this X-ray, one has a sense that the right capital femoral epiphysis does not align with the femoral neck in the same way as it does on the left side, suggesting slippage.
FAST Exam to Diagnose Subcapsular Renal Hematoma
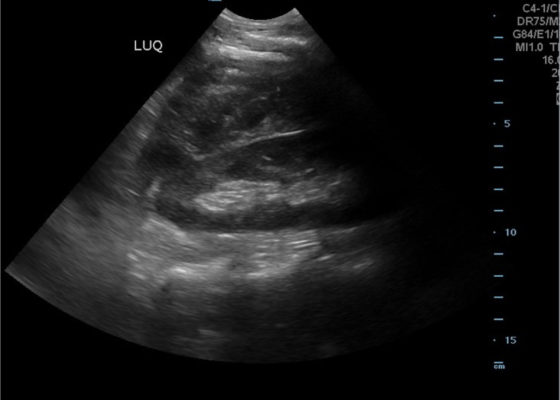
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NP8DA bedside point of care ultrasound FAST exam was performed revealing a left subcapsular renal hematoma. The hematoma was a non-compressing hematoma, evidenced by preserved renal contour with the hematoma labeled with a red H and the normal renal contour labeled with a green K. Additionally, cortical necrosis and ischemia can be characterized by a dark, hypoechogenic renal cortex on ultrasonography with a decrease in flow to the cortex on color doppler which was not seen on this patient, providing further evidence that the hematoma was non-compressing. The hematoma was concluded to be an acute process due to its hypoechoic appearance with some mixed ultrasonographic echoes caused by the early deposit of fibrin.
Right Upper Quadrant Pain in a World Explorer
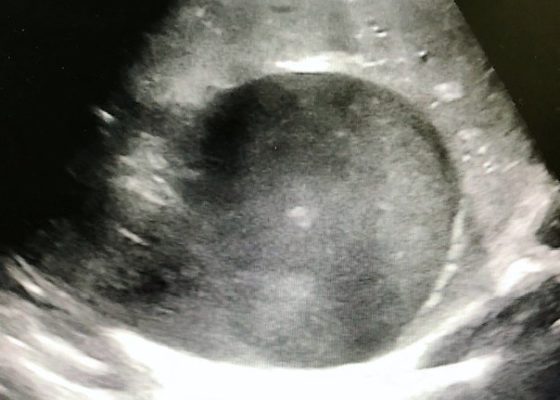
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QP9DThe ultrasound images show the abscess, which is a large, circular, hypoechoic mass outlined in blue in the center of the image. The abscess is surrounded by the hyperechoic and heterogeneous liver tissue.
For better delineation of the abscess, a CT was ordered. The axial CT scan image shows the liver abscess, which appears as a hypodense, ovoid, intrahepatic fluid collection within the liver parenchyma. The size of the abscess has been annotated with a dotted line measuring 194.9 mm x 166.2 mm.