Procedures
Laceration Repair for Emergency Physicians
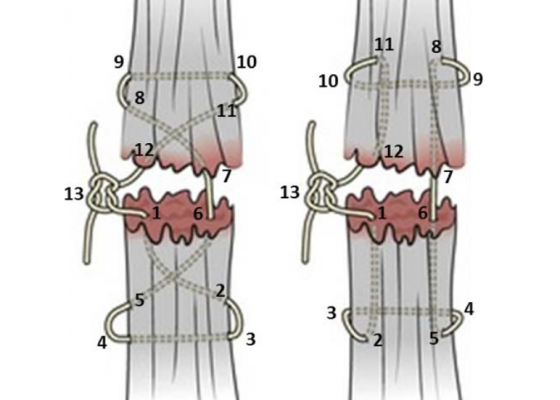
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TP7KBy the end of this educational session, the learner will: 1) understand indications and contraindications for suture repair of lacerations, 2) compare when various types of wound repair are appropriate: such as sutures, staples, tissue adhesive and tissue tape, as well as what size of suture material is appropriate depending on the location of the laceration on the body, 3) list the appropriate types and sizes of suture for various locations and types of lacerations, 4) understand the definitions of the three types of wound closure (primary, secondary and delayed primary) and when they are appropriate, 5) understand the basics of local anesthetic including which anesthetic to use and the maximum dose for each, 6) understand when sutures should be removed, 7) list various suturing techniques and their indications, and 8) improve comfort levels in performing various suturing techniques including: simple interrupted, horizontal mattress, vertical mattress, and corner repair. If desired, instructors can individually assess the learner sutures using the attached complete validated suture checklist to show proficiency in these techniques. Please see the brief wrap-up section at the end of the manuscript.
A Simulation Model for Extensor Tendon Repair
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VS7XBy the end of this educational session, the learner will be able to: 1) List the indications for extensor tendon repair in the emergency department, 2) recognize the indications for referral to orthopedic or hand surgery, 3) list the risks and benefits of emergency department extensor tendon repair, 4) perform an appropriate physical examination for a patient with a potential extensor tendon laceration, 5) list the maximum time limit of tourniquet application for this procedure, 6) list the materials needed for extensor tendon repair in the emergency department, 7) successfully repair a completely severed extensor tendon using four different techniques: horizontal mattress, figure of eight, modified Kessler and modified Bunnell, and 8) describe the appropriate splinting of a repaired extensor tendon.
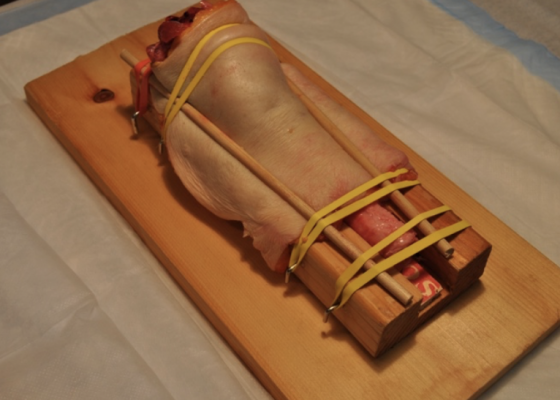
Realistic Chest Tube Simulator Using Pork Belly with Skin
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8R03JBy the end of this instructional session learners will be able to: 1) discuss the indications, contraindications, and complications associated with chest tube thoracostomy, 2) competently perform chest tube insertion on a simulator, and 3) properly secure chest tube.
Emergency Surgical Airway Model for Procedural Skills Simulation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8M921At the end of this educational session, learners will be able to: 1) practice the manual and cognitive skills necessary to perform a successful and rapid surgical cricothyrotomy, and 2) successfully complete a cricothyrotomy within a time frame of 90 seconds.
Development of a Head and Neck Regional Anesthesia Task Trainer for Emergency Medicine Learners
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8T595In participating in the educational session associated with this task trainer, the learner will:
1) Identify landmarks for the following nerve blocks: Infraorbital, Supraorbital (V1), Mental, Periauricular
2) Demonstrate the appropriate technique for anesthetic injection for each of these nerve blocks
3) Map the distribution of regional anesthesia expected from each nerve block
4) Apply the indications and contraindications for each regional nerve block
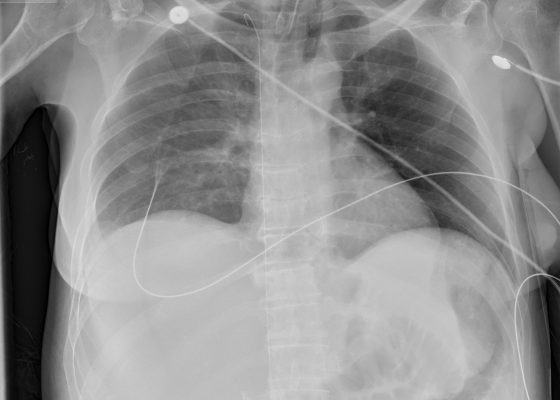
The Lost Guidewire
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82P4MInitial chest radiograph shows a guidewire in the inferior vena cava (IVC), superior vena cava (SVC), and right IJ veins.
Edible Cricothyrotomy Model: A Low-Cost Alternative to Pig Tracheas and Plastic Models for Teaching Cricothyrotomy
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8C88SAn edible cricothyrotomy model was built for each participant from the ingredients listed above. An educational session was developed to test the EC in comparison to the more traditional pig trachea (PT) and plastic model (PM). A pre- and post-survey was administered to participants to assess the usability and realism of the models as well as the learners’ comfort with the procedure. During the session, a lecture was given, and then participants rotated to all three models and were videotaped and timed performing a scalpel-finger-bougie cricothyrotomy. Times to successful completion, participant satisfaction with the models, and cost of the models were compared.
The Bubble-Wrap Peritonsillar Abscess Model
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87G6VThis model uses bubble wrap, zip ties, chicken broth and liquid latex to simulate a peritonsillar abscess. Learners are then able to perform a needle aspiration of the simulated abscess from start to the end with no risk to a live patient.