Posts by JETem
Perforated Gastric Ulcer with Intra-abdominal Abscess
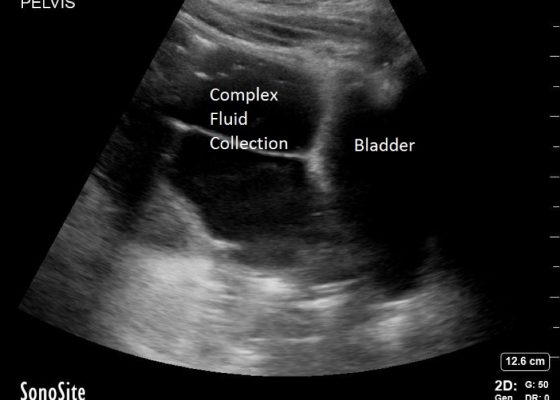
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82H0CBedside ultrasound revealed a large volume of free fluid in the right upper quadrant and in the pelvis. The fluid appeared complex with multiple septations. Its appearance was not consistent with ascites or acute intra-abdominal free fluid due to striations and pockets.
Use of Bedside Compression Ultrasonography for Diagnosis of Deep Venous Thrombosis
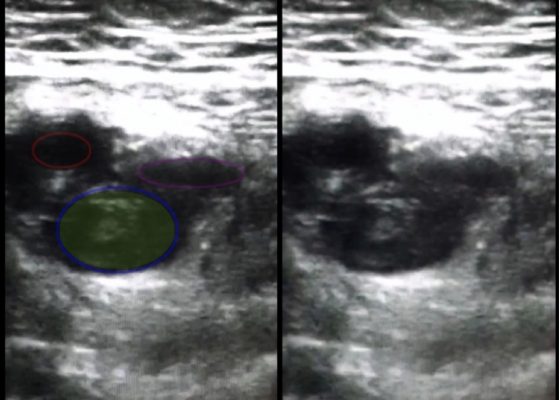
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J81G94As shown in the still image of the performed ultrasound, a transverse view of the proximal-thigh revealed a visible thrombus (green shading) occluding the lumen of the left common femoral vein (blue ring), which was non-compressible when direct pressure was applied to the probe. Also visible is a patent and compressible branch of the common femoral vein (purple ring) and the femoral artery (red ring), highlighted by its thick vessel wall and pulsatile motion.
Open Pneumothorax
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88036A large chest wound was clinically obvious. A chest radiograph performed after intubation showed subcutaneous emphysema, an anterior rib fracture, and a right-sided pneumothorax. He was then taken to the operating room for further management.
Dense MCA Sign
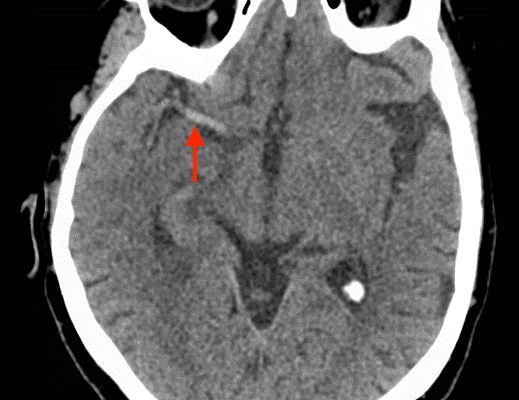
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8CS66A non-contrast computed tomography (CT) scan showed a hyperdensity along the right middle cerebral artery (MCA) consistent with acute thrombus. The red arrow highlights the hyperdensity in the annotated image.
Supracondylar Fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8492PHistory of present illness: A 15-year-old male presented to the emergency department with right elbow pain after falling off a skateboard. The patient denied a decrease in strength or sensation but did endorse paresthesias to his hand. On exam, the patient had an obvious deformity of his right elbow with tenderness to palpation and decreased range of motion at the
Development of a Head and Neck Regional Anesthesia Task Trainer for Emergency Medicine Learners
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8T595In participating in the educational session associated with this task trainer, the learner will:
1) Identify landmarks for the following nerve blocks: Infraorbital, Supraorbital (V1), Mental, Periauricular
2) Demonstrate the appropriate technique for anesthetic injection for each of these nerve blocks
3) Map the distribution of regional anesthesia expected from each nerve block
4) Apply the indications and contraindications for each regional nerve block
The Halloween Lateral Canthotomy Model
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8GW2NThe purpose of the model is to teach residents and students how to perform lateral canthotomy and to achieve competency in their skills.
Emed-Opoly: Echocardiography
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8PC77By the end of this session, the learner will be able to:
1) Recognize normal and abnormal left heart global function
2) Recognize normal and abnormal right heart global function
3) Recognize pericardial effusions and pericardial tamponade