Posts by JETem
Bezoars: An Interesting Case of Abdominal Pain
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VD1VComputed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with oral and intravenous contrast was ordered to evaluate her symptoms. The CT showed three large collections of ingested material seen as hypodense material with circular rings surrounded by the hyperdense oral contrast (see red outlines). These findings are consistent with bezoars, the largest of which measured 11.5 x 7.8 cm. There was also thickening of the gastric wall (see blue outline), most notably at the pylorus, consistent with partial obstruction.
Medial Subtalar Dislocation: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QP9DOn examination, the patient had a significant deformity to his left foot and ankle. His left foot was pointed medially. His distal left tibia and fibula were visible and palpable upon inspection, with the overlying skin completely intact. There was no neurovascular compromise of the foot. X-ray demonstrated a subtalar dislocation of the left ankle (green arrow) and significant widening of the tibiotalar joint space (yellow arrow). There was associated soft tissue swelling but no acute displaced fractures were identified.
The Elusive Pheo: A Case Report of Pheochromocytoma in the Emergency Department
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KW63ED work-up: BMP within normal limits (WNL), white blood cell (WBC) 27.4, ECG showed sinus tachycardia, nonspecific ST segment abnormalities, BNP and troponin were within normal limits, HR 146 beats/minute, CT abdomen/pelvis showed a 10-cm-heterogenous enhancing left adrenal mass (anterior-posterior view [shown in red], lateral view [shown in blue]).
Traumatic Diaphragmatic Rupture – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8G64HChest X-ray showed an elevated left hemi-diaphragm with superior displacement of a portion of intra-abdominal contents presumed to be the stomach (green arrowheads) with associated rightward mediastinal shift (yellow arrows). The diagnosis was confirmed by CT. Computed tomography imaging of the chest showed a large, left diaphragmatic defect measuring approximately 5.5 cm with herniation of the upper half of the stomach through the defect. The fundus of the stomach (blue arrow) herniated superiorly through the ruptured diaphragm (red arrow).
Classic Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BD16The pelvis X-ray demonstrates a widened right capital femoral epiphysis (more than 2 mm) that is typical of a slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE).1 The yellow highlight outlines this area of widening.
The classic Klein’s line (orange lines) is often inaccurate and even difficult to draw with certainty.1 Nevertheless, in this X-ray, one has a sense that the right capital femoral epiphysis does not align with the femoral neck in the same way as it does on the left side, suggesting slippage.
FAST Exam to Diagnose Subcapsular Renal Hematoma
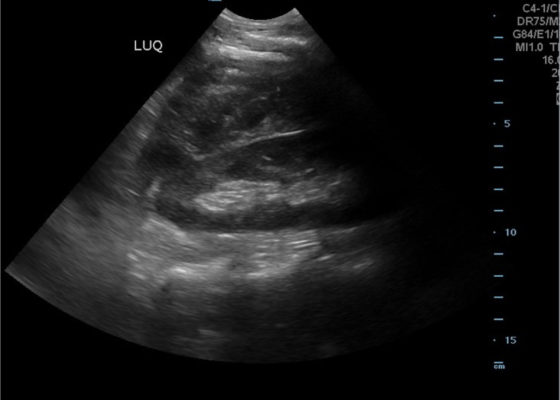
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NP8DA bedside point of care ultrasound FAST exam was performed revealing a left subcapsular renal hematoma. The hematoma was a non-compressing hematoma, evidenced by preserved renal contour with the hematoma labeled with a red H and the normal renal contour labeled with a green K. Additionally, cortical necrosis and ischemia can be characterized by a dark, hypoechogenic renal cortex on ultrasonography with a decrease in flow to the cortex on color doppler which was not seen on this patient, providing further evidence that the hematoma was non-compressing. The hematoma was concluded to be an acute process due to its hypoechoic appearance with some mixed ultrasonographic echoes caused by the early deposit of fibrin.
Right Upper Quadrant Pain in a World Explorer
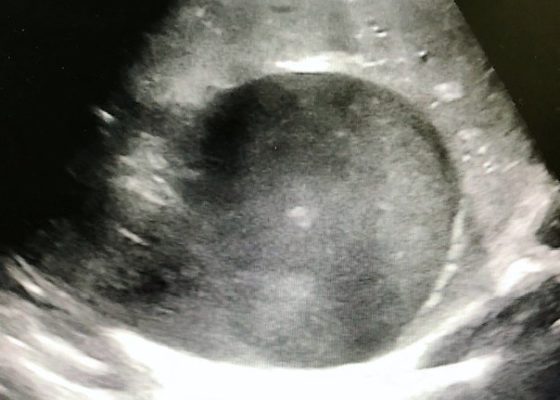
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QP9DThe ultrasound images show the abscess, which is a large, circular, hypoechoic mass outlined in blue in the center of the image. The abscess is surrounded by the hyperechoic and heterogeneous liver tissue.
For better delineation of the abscess, a CT was ordered. The axial CT scan image shows the liver abscess, which appears as a hypodense, ovoid, intrahepatic fluid collection within the liver parenchyma. The size of the abscess has been annotated with a dotted line measuring 194.9 mm x 166.2 mm.